Nuclear receptor: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
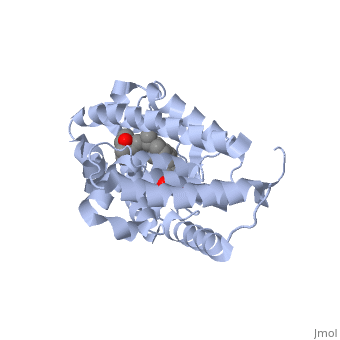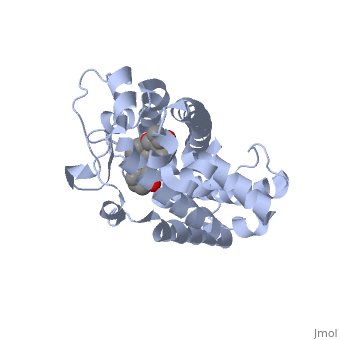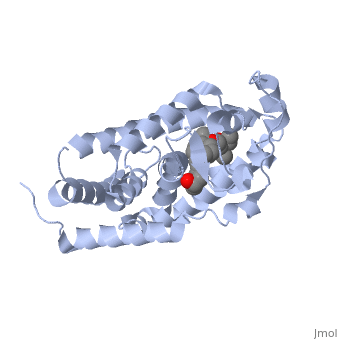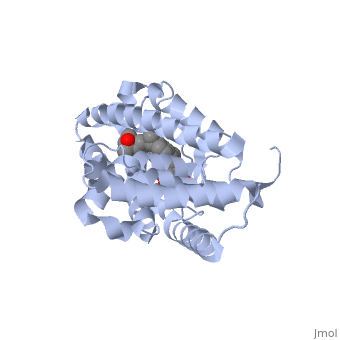
The structure of the LBD is strongly conserved throughout the familly of nuclear receptors. | The structure of the LBD is strongly conserved throughout the familly of nuclear receptors. | ||
It is a globular domain<scene name='Nuclear_receptor/Nr-lbd-/1'>well folded</scene> | It is a globular domain | ||
<scene name='Nuclear_receptor/Nr-lbd-/1'>well folded</scene> | |||
and composed of a beta-sheet, and 12 alpha-helices arranged in a three layered sandwich. | and composed of a beta-sheet, and 12 alpha-helices arranged in a three layered sandwich. | ||
Revision as of 12:05, 6 September 2012
the nuclear receptors facts book [1]
StructureStructure
DBD (DNA Binding Domain)DBD (DNA Binding Domain)
LBD (Ligand Binding Domain)LBD (Ligand Binding Domain)
The structure of the LBD is strongly conserved throughout the familly of nuclear receptors. It is a globular domain and composed of a beta-sheet, and 12 alpha-helices arranged in a three layered sandwich.
|
| ||||||||||
- ↑ Vincent Laudet, Hinrich Gronemeyer, "The nuclear receptor factsbook", Publisher Academic Press, 2002