Ozonolysis: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Eric Martz (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Reaction== | ==Reaction== | ||
<applet load='1ea5' size=' | <applet load='1ea5' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Ozonolysis Rxn' scene='Ozonolysis/Initial/1'/> | ||
[[Image:Ozonolysis stepone.jpg]] | [[Image:Ozonolysis stepone.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 12:18, 17 February 2016
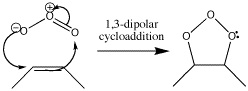
Ozonolysis is a type of cycloaddition which destroys bonds. It starts with a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition but eventually becomes a method of cleaving π bonds in an oxidative fashion, so that they end up as two carbonyl groups. The reagent for this reaction is ozone, O3.
ReactionReaction
|
- Here are the electron pushing .
- We can also watch the , or the
- Reaction with , or the
- Reaction with .
AcknowledgementsAcknowledgements
The animations of the ozonolysis reaction, as well as the 2D images of the reaction mechanism, were created by Nick Greeves. Many more reactions are viewable in an intuitive manner at http://www.chemtube3d.com.