1e6m: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
< | ==TWO-COMPONENT SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION SYSTEM D57A MUTANT OF CHEY== | ||
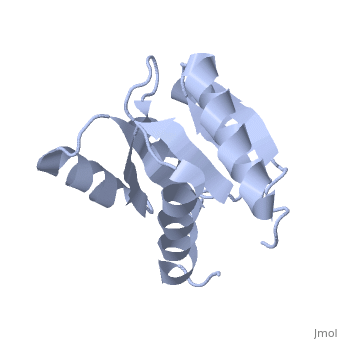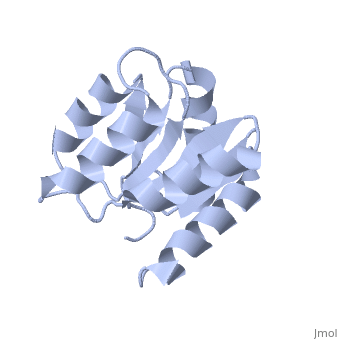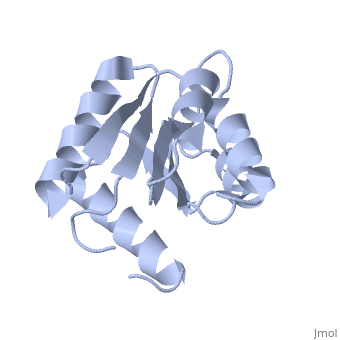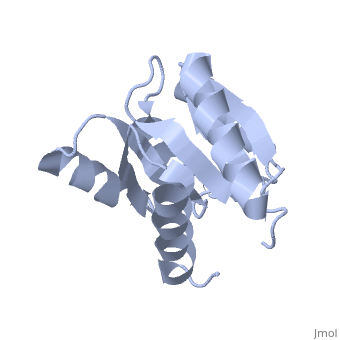
<StructureSection load='1e6m' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1e6m]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 1.70Å' scene=''> | |||
You may | == Structural highlights == | ||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1e6m]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Escherichia_coli_K-12 Escherichia coli K-12]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1E6M OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1E6M FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 1.7Å</td></tr> | |||
- | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1e6m FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1e6m OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1e6m PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1e6m RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1e6m PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1e6m ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | ||
</table> | |||
== Function == | |||
[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CHEY_ECOLI CHEY_ECOLI] Involved in the transmission of sensory signals from the chemoreceptors to the flagellar motors. In its active (phosphorylated or acetylated) form, CheY exhibits enhanced binding to a switch component, FliM, at the flagellar motor which induces a change from counterclockwise to clockwise flagellar rotation. Overexpression of CheY in association with MotA and MotB improves motility of a ycgR disruption, suggesting there is an interaction (direct or indirect) between the c-di-GMP-binding flagellar brake protein and the flagellar stator.<ref>PMID:20346719</ref> | |||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | |||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | |||
Check<jmol> | |||
<jmolCheckbox> | |||
<scriptWhenChecked>; select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/e6/1e6m_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | |||
<scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | |||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | |||
</jmolCheckbox> | |||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=1e6m ConSurf]. | |||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
The signal transduction protein CheY displays an alpha/beta-parallel polypeptide folding, including a highly unstable helix alpha4 and a strongly charged active site. Helix alpha4 has been shown to adopt various positions and conformations in different crystal structures, suggesting that it is a mobile segment. Furthermore, the instability of this helix is believed to have functional significance because it is involved in protein-protein contacts with the transmitter protein kinase CheA, the target protein FliM and the phosphatase CheZ. The active site of CheY comprises a cluster of three aspartic acid residues and a lysine residue, all of which participate in the binding of the Mg(2+) needed for the protein activation. Two steps were followed to study the activation mechanism of CheY upon phosphorylation: first, we independently substituted the three aspartic acid residues in the active site with alanine; second, several mutations were designed in helix alpha 4, both to increase its level of stability and to improve its packing against the protein core. The structural and thermodynamic analysis of these mutant proteins provides further evidence of the connection between the active-site area and helix alpha 4, and helps to understand how small movements at the active site are transmitted and amplified to the protein surface. | |||
Towards understanding a molecular switch mechanism: thermodynamic and crystallographic studies of the signal transduction protein CheY.,Sola M, Lopez-Hernandez E, Cronet P, Lacroix E, Serrano L, Coll M, Parraga A J Mol Biol. 2000 Oct 20;303(2):213-25. PMID:11023787<ref>PMID:11023787</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
<div class="pdbe-citations 1e6m" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | |||
==See Also== | |||
*[[Chemotaxis protein|Chemotaxis protein]] | |||
*[[Chemotaxis protein 3D structures|Chemotaxis protein 3D structures]] | |||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
__TOC__ | |||
== | </StructureSection> | ||
[[Category: Escherichia coli K-12]] | |||
[[Category: Large Structures]] | |||
== | [[Category: Coll M]] | ||
< | [[Category: Cronet P]] | ||
[[Category: Escherichia coli]] | [[Category: Lacroix E]] | ||
[[Category: Coll | [[Category: Lopez-Hernandez E]] | ||
[[Category: Cronet | [[Category: Parraga A]] | ||
[[Category: Lacroix | [[Category: Serrano L]] | ||
[[Category: Lopez-Hernandez | [[Category: Sola M]] | ||
[[Category: Parraga | |||
[[Category: Serrano | |||
[[Category: Sola | |||
Latest revision as of 11:47, 9 May 2024
TWO-COMPONENT SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION SYSTEM D57A MUTANT OF CHEYTWO-COMPONENT SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION SYSTEM D57A MUTANT OF CHEY
Structural highlights
FunctionCHEY_ECOLI Involved in the transmission of sensory signals from the chemoreceptors to the flagellar motors. In its active (phosphorylated or acetylated) form, CheY exhibits enhanced binding to a switch component, FliM, at the flagellar motor which induces a change from counterclockwise to clockwise flagellar rotation. Overexpression of CheY in association with MotA and MotB improves motility of a ycgR disruption, suggesting there is an interaction (direct or indirect) between the c-di-GMP-binding flagellar brake protein and the flagellar stator.[1] Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedThe signal transduction protein CheY displays an alpha/beta-parallel polypeptide folding, including a highly unstable helix alpha4 and a strongly charged active site. Helix alpha4 has been shown to adopt various positions and conformations in different crystal structures, suggesting that it is a mobile segment. Furthermore, the instability of this helix is believed to have functional significance because it is involved in protein-protein contacts with the transmitter protein kinase CheA, the target protein FliM and the phosphatase CheZ. The active site of CheY comprises a cluster of three aspartic acid residues and a lysine residue, all of which participate in the binding of the Mg(2+) needed for the protein activation. Two steps were followed to study the activation mechanism of CheY upon phosphorylation: first, we independently substituted the three aspartic acid residues in the active site with alanine; second, several mutations were designed in helix alpha 4, both to increase its level of stability and to improve its packing against the protein core. The structural and thermodynamic analysis of these mutant proteins provides further evidence of the connection between the active-site area and helix alpha 4, and helps to understand how small movements at the active site are transmitted and amplified to the protein surface. Towards understanding a molecular switch mechanism: thermodynamic and crystallographic studies of the signal transduction protein CheY.,Sola M, Lopez-Hernandez E, Cronet P, Lacroix E, Serrano L, Coll M, Parraga A J Mol Biol. 2000 Oct 20;303(2):213-25. PMID:11023787[2] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||