2g2u: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
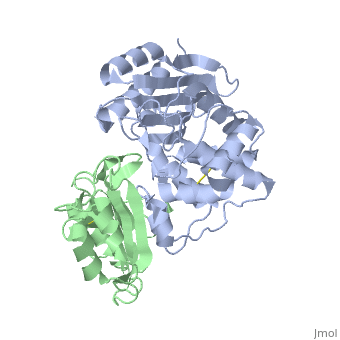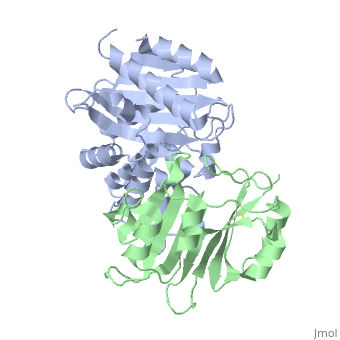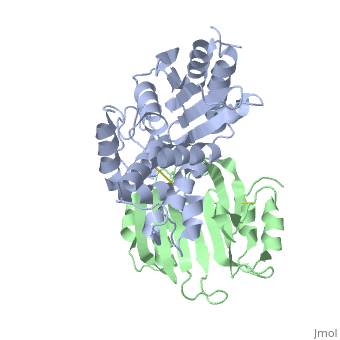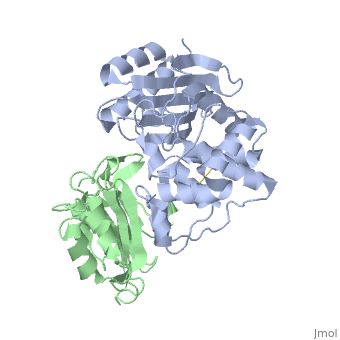
==Crystal Structure of the SHV-1 Beta-lactamase/Beta-lactamase inhibitor protein (BLIP) complex== | |||
<StructureSection load='2g2u' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2g2u]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 1.60Å' scene=''> | |||
== Structural highlights == | |||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2g2u]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Klebsiella_pneumoniae Klebsiella pneumoniae] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Streptomyces_clavuligerus Streptomyces clavuligerus]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2G2U OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2G2U FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 1.6Å</td></tr> | |||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2g2u FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2g2u OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2g2u PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2g2u RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2g2u PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2g2u ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
== Function == | |||
[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/BLA1_KLEPN BLA1_KLEPN] | |||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | |||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | |||
Check<jmol> | |||
<jmolCheckbox> | |||
<scriptWhenChecked>; select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/g2/2g2u_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | |||
<scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview03.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | |||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | |||
</jmolCheckbox> | |||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=2g2u ConSurf]. | |||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
Beta-lactamase inhibitor protein (BLIP) binds a variety of class A beta-lactamases with affinities ranging from micromolar to picomolar. Whereas the TEM-1 and SHV-1 beta-lactamases are almost structurally identical, BLIP binds TEM-1 approximately 1000-fold tighter than SHV-1. Determining the underlying source of this affinity difference is important for understanding the molecular basis of beta-lactamase inhibition and mechanisms of protein-protein interface specificity and affinity. Here we present the 1.6A resolution crystal structure of SHV-1.BLIP. In addition, a point mutation was identified, SHV D104E, that increases SHV.BLIP binding affinity from micromolar to nanomolar. Comparison of the SHV-1.BLIP structure with the published TEM-1.BLIP structure suggests that the increased volume of Glu-104 stabilizes a key binding loop in the interface. Solution of the 1.8A SHV D104K.BLIP crystal structure identifies a novel conformation in which this binding loop is removed from the interface. Using these structural data, we evaluated the ability of EGAD, a program developed for computational protein design, to calculate changes in the stability of mutant beta-lactamase.BLIP complexes. Changes in binding affinity were calculated within an error of 1.6 kcal/mol of the experimental values for 112 mutations at the TEM-1.BLIP interface and within an error of 2.2 kcal/mol for 24 mutations at the SHV-1.BLIP interface. The reasonable success of EGAD in predicting changes in interface stability is a promising step toward understanding the stability of the beta-lactamase.BLIP complexes and computationally assisted design of tight binding BLIP variants. | |||
Structural and computational characterization of the SHV-1 beta-lactamase-beta-lactamase inhibitor protein interface.,Reynolds KA, Thomson JM, Corbett KD, Bethel CR, Berger JM, Kirsch JF, Bonomo RA, Handel TM J Biol Chem. 2006 Sep 8;281(36):26745-53. Epub 2006 Jun 29. PMID:16809340<ref>PMID:16809340</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
<div class="pdbe-citations 2g2u" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | |||
== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Beta-lactamase 3D structures|Beta-lactamase 3D structures]] | |||
*[[TEM1-beta-Lactamase/beta-lactamase Inhibitor Protein (BLIP)|TEM1-beta-Lactamase/beta-lactamase Inhibitor Protein (BLIP)]] | |||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
__TOC__ | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
[[Category: Klebsiella pneumoniae]] | [[Category: Klebsiella pneumoniae]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
[[Category: Streptomyces clavuligerus]] | [[Category: Streptomyces clavuligerus]] | ||
[[Category: Berger | [[Category: Berger JM]] | ||
[[Category: Bethel | [[Category: Bethel CR]] | ||
[[Category: Bonomo | [[Category: Bonomo RA]] | ||
[[Category: Corbett | [[Category: Corbett KD]] | ||
[[Category: Handel | [[Category: Handel TM]] | ||
[[Category: Kirsch | [[Category: Kirsch JF]] | ||
[[Category: Reynolds | [[Category: Reynolds KA]] | ||
[[Category: Thomson | [[Category: Thomson JM]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:37, 9 October 2024
Crystal Structure of the SHV-1 Beta-lactamase/Beta-lactamase inhibitor protein (BLIP) complexCrystal Structure of the SHV-1 Beta-lactamase/Beta-lactamase inhibitor protein (BLIP) complex
Structural highlights
FunctionEvolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedBeta-lactamase inhibitor protein (BLIP) binds a variety of class A beta-lactamases with affinities ranging from micromolar to picomolar. Whereas the TEM-1 and SHV-1 beta-lactamases are almost structurally identical, BLIP binds TEM-1 approximately 1000-fold tighter than SHV-1. Determining the underlying source of this affinity difference is important for understanding the molecular basis of beta-lactamase inhibition and mechanisms of protein-protein interface specificity and affinity. Here we present the 1.6A resolution crystal structure of SHV-1.BLIP. In addition, a point mutation was identified, SHV D104E, that increases SHV.BLIP binding affinity from micromolar to nanomolar. Comparison of the SHV-1.BLIP structure with the published TEM-1.BLIP structure suggests that the increased volume of Glu-104 stabilizes a key binding loop in the interface. Solution of the 1.8A SHV D104K.BLIP crystal structure identifies a novel conformation in which this binding loop is removed from the interface. Using these structural data, we evaluated the ability of EGAD, a program developed for computational protein design, to calculate changes in the stability of mutant beta-lactamase.BLIP complexes. Changes in binding affinity were calculated within an error of 1.6 kcal/mol of the experimental values for 112 mutations at the TEM-1.BLIP interface and within an error of 2.2 kcal/mol for 24 mutations at the SHV-1.BLIP interface. The reasonable success of EGAD in predicting changes in interface stability is a promising step toward understanding the stability of the beta-lactamase.BLIP complexes and computationally assisted design of tight binding BLIP variants. Structural and computational characterization of the SHV-1 beta-lactamase-beta-lactamase inhibitor protein interface.,Reynolds KA, Thomson JM, Corbett KD, Bethel CR, Berger JM, Kirsch JF, Bonomo RA, Handel TM J Biol Chem. 2006 Sep 8;281(36):26745-53. Epub 2006 Jun 29. PMID:16809340[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||