Clashes: Difference between revisions
Eric Martz (talk | contribs) |
Eric Martz (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (34 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''Clashes'' in protein models, also called ''steric clashes'', occur when two | <imagemap> | ||
Image:Rama-youtube-EM.gif|right | |||
default [[Tutorial:Ramachandran principle and phi psi angles]] | |||
</imagemap> | |||
''Clashes'' in protein models, also called ''steric clashes'', occur when two atoms, not covalently bonded to each other, are impossibly close to each other. This happens when the [[van der Waals radii]] of the atoms overlap; that is, when two atoms are occupying the same space. Clashes typically occur in lower [[resolution]] models due to the difficulties of obeying all chemical constraints while optimizing the fit of the model to the experimental data. Clashes are more common in [[X-ray crystallography|X-ray crystallographic]] models with [[resolution|resolutions]] of 3.0 Å or worse, or in [[cryo-EM]] models. ([[NMR]] models generally lack clashes because they are forced to obey chemical constraints.) | |||
==Clashes Dictate Protein Secondary Structure== | ==Clashes Dictate Protein Secondary Structure== | ||
The prevalence of [[alpha helix|alpha helices]] and [[sheets in Proteins|beta strands]] in the [[secondary structure]] of proteins results from the avoidance of clashes in the polypeptide chain, as embodied in the Ramachandran Principle. Interactive visualizations of clashes during rotations of bonds in polypeptide chains are available at | The prevalence of [[alpha helix|alpha helices]] and [[sheets in Proteins|beta strands]] in the [[secondary structure]] of proteins results from the avoidance of clashes in the polypeptide chain, as embodied in the Ramachandran Principle. Interactive visualizations of clashes during rotations of bonds in polypeptide chains are available at | ||
[[Tutorial:Ramachandran principle and phi psi angles]]. | [[Tutorial:Ramachandran principle and phi psi angles]]. Several other related tutorials and perspectives will be found at [[Dihedral/Index]]. | ||
==Clashes vs. Model Quality== | ==Clashes vs. Model Quality== | ||
The presence of too many clashes in a model calls into question | The presence of too many clashes in a model calls its reliability into question. All models submitted to the Protein Data Bank (PDB) are analyzed by [[MolProbity]], which adds hydrogen atoms (where absent), determines a clash score ("clashscore"), and ranks the clashscore relative to other models of the same resolution. The clashscore is the number of clashes per 1,000 atoms (including hydrogens). A clash is considered to occur when the van der Waals radii overlap by ≥ 0.4 Å<ref>[https://www.wwpdb.org/validation/2017/EMValidationReportHelp#close_contacts Too-Close Contacts] at the World Wide Protein Data Bank.</ref>. Each [[wwPDB]] entry has an extensive Validation Report<ref>[https://www.wwpdb.org/validation/validation-reports wwPDB Validation Reports].</ref> that includes an analysis of clashes. Here are a couple of examples: | ||
* [[6zx4]], an X-ray model of resolution 0.96 Å, contains 5,850 atoms including hydrogens. 6 clashes were present with atomic overlaps in the range 0.41-0.49 Å. The clashscore is thus 6/5.8 = 1.0. This placed it in about the 90th percentile (90% of the compared models have more clashes) of 1,321 models with resolutions of 0.86-1.06 Å. [https://files.rcsb.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zx/6zx4/6zx4_full_validation.pdf Full Validation Report]. Caution: the percentile rank is based on a reference dataset from the time of deposition (or earlier?). 6zx4 was deposited in July, 2020. The validation reference dataset had about 70% of the X-ray entries in the stated resolution range 0.86-1.06 Å that were present in the wwPDB in November, 2021. | |||
* [[6ef8]], a cryo-EM model of resolution 3.7 Å, contains 22,911 non-hydrogen atoms. MolProbity added 20,895 hydrogens for a total of 43,806 atoms. 558 clashes were present with atomic overlaps in the range 0.4 to 1.47 Å. The clashscore is thus 558/43.8 = 13. This placed it in about the 35th percentile (only 35% of the compared models have more clashes) among the clashscores for all cryo-EM models. [https://files.rcsb.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ef/6ef8/6ef8_full_validation.pdf Full Validation Report]. Caution: the percentile rank is based on a reference dataset from the time of deposition (or earlier?). 6ef8 was deposited in August, 2018. The reference dataset had about half of the total cryo-EM entries in the wwPDB in November, 2021. Re-running the validation in November, 2021 at the [https://validate-rcsb-1.wwpdb.org/ wwPDB Validation Service] did not increase the size of the reference dataset. | |||
==Visualization of Clashes== | ==Visualization of Clashes== | ||
*MolProbity offers visualization of clashes in | <imagemap> | ||
*Jmol offers visualization of clashes | Image:Rama-youtube-EM.gif|right | ||
default [[Tutorial:Ramachandran principle and phi psi angles]] | |||
</imagemap> | |||
*Clashes that form and recede in real time during rotation of polypeptide phi and psi bonds can be seen at [[Tutorial:Ramachandran principle and phi psi angles]]. | |||
*For a model of your choice: | |||
**MolProbity offers visualization of clashes in [http://nglviewer.org NGL Viewer]. Caution: In November, 2021, the percentile rank of the clashscore is based on a very old reference dataset from 2007 or earlier. | |||
**Jmol offers visualization of clashes in its [https://chemapps.stolaf.edu/jmol/jsmol/validation.htm Validation Tools]. Jmol obtains clash data from the [[wwPDB]] (see "load =xxxx/val" under [https://chemapps.stolaf.edu/jmol/docs/#annotations Annotations]). | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| Line 20: | Line 34: | ||
*[[Quality assessment for molecular models]] | *[[Quality assessment for molecular models]] | ||
*[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Steric_effects Steric Effects in Wikipedia] | *[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Steric_effects Steric Effects in Wikipedia] | ||
==Notes and References== | |||
<references /> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:39, 20 May 2024
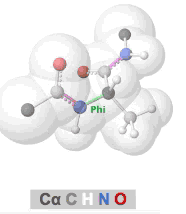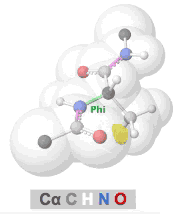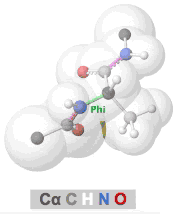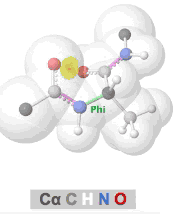
Clashes in protein models, also called steric clashes, occur when two atoms, not covalently bonded to each other, are impossibly close to each other. This happens when the van der Waals radii of the atoms overlap; that is, when two atoms are occupying the same space. Clashes typically occur in lower resolution models due to the difficulties of obeying all chemical constraints while optimizing the fit of the model to the experimental data. Clashes are more common in X-ray crystallographic models with resolutions of 3.0 Å or worse, or in cryo-EM models. (NMR models generally lack clashes because they are forced to obey chemical constraints.)
Clashes Dictate Protein Secondary StructureClashes Dictate Protein Secondary Structure
The prevalence of alpha helices and beta strands in the secondary structure of proteins results from the avoidance of clashes in the polypeptide chain, as embodied in the Ramachandran Principle. Interactive visualizations of clashes during rotations of bonds in polypeptide chains are available at Tutorial:Ramachandran principle and phi psi angles. Several other related tutorials and perspectives will be found at Dihedral/Index.
Clashes vs. Model QualityClashes vs. Model Quality
The presence of too many clashes in a model calls its reliability into question. All models submitted to the Protein Data Bank (PDB) are analyzed by MolProbity, which adds hydrogen atoms (where absent), determines a clash score ("clashscore"), and ranks the clashscore relative to other models of the same resolution. The clashscore is the number of clashes per 1,000 atoms (including hydrogens). A clash is considered to occur when the van der Waals radii overlap by ≥ 0.4 Å[1]. Each wwPDB entry has an extensive Validation Report[2] that includes an analysis of clashes. Here are a couple of examples:
- 6zx4, an X-ray model of resolution 0.96 Å, contains 5,850 atoms including hydrogens. 6 clashes were present with atomic overlaps in the range 0.41-0.49 Å. The clashscore is thus 6/5.8 = 1.0. This placed it in about the 90th percentile (90% of the compared models have more clashes) of 1,321 models with resolutions of 0.86-1.06 Å. Full Validation Report. Caution: the percentile rank is based on a reference dataset from the time of deposition (or earlier?). 6zx4 was deposited in July, 2020. The validation reference dataset had about 70% of the X-ray entries in the stated resolution range 0.86-1.06 Å that were present in the wwPDB in November, 2021.
- 6ef8, a cryo-EM model of resolution 3.7 Å, contains 22,911 non-hydrogen atoms. MolProbity added 20,895 hydrogens for a total of 43,806 atoms. 558 clashes were present with atomic overlaps in the range 0.4 to 1.47 Å. The clashscore is thus 558/43.8 = 13. This placed it in about the 35th percentile (only 35% of the compared models have more clashes) among the clashscores for all cryo-EM models. Full Validation Report. Caution: the percentile rank is based on a reference dataset from the time of deposition (or earlier?). 6ef8 was deposited in August, 2018. The reference dataset had about half of the total cryo-EM entries in the wwPDB in November, 2021. Re-running the validation in November, 2021 at the wwPDB Validation Service did not increase the size of the reference dataset.
Visualization of ClashesVisualization of Clashes

- Clashes that form and recede in real time during rotation of polypeptide phi and psi bonds can be seen at Tutorial:Ramachandran principle and phi psi angles.
- For a model of your choice:
- MolProbity offers visualization of clashes in NGL Viewer. Caution: In November, 2021, the percentile rank of the clashscore is based on a very old reference dataset from 2007 or earlier.
- Jmol offers visualization of clashes in its Validation Tools. Jmol obtains clash data from the wwPDB (see "load =xxxx/val" under Annotations).
See AlsoSee Also
- Tutorial:Ramachandran principle and phi psi angles
- Dihedral/Index which has links to many tutorials and resources about the Ramachandran principle, and phi and psi angles in proteins.
- Ramachandran Plot
- Quality assessment for molecular models
- Steric Effects in Wikipedia
Notes and ReferencesNotes and References
- ↑ Too-Close Contacts at the World Wide Protein Data Bank.
- ↑ wwPDB Validation Reports.