2kho: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
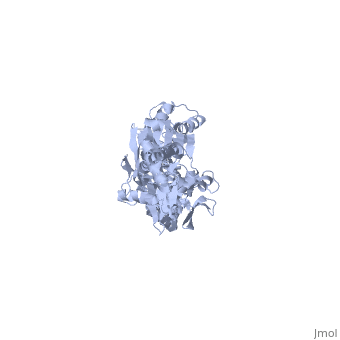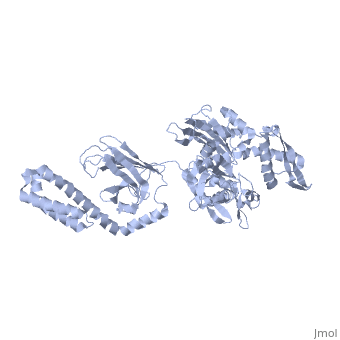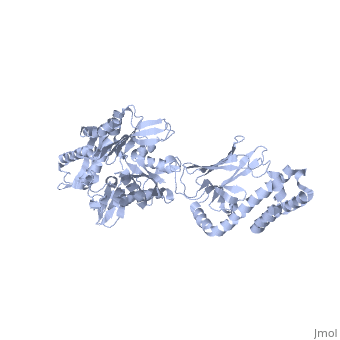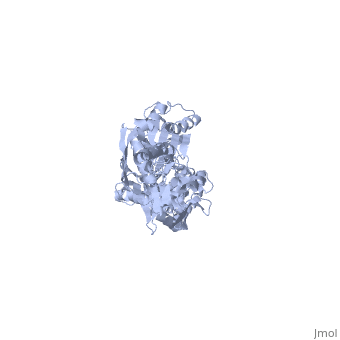
==NMR-RDC / XRAY structure of E. coli HSP70 (DNAK) chaperone (1-605) complexed with ADP and substrate== | ==NMR-RDC / XRAY structure of E. coli HSP70 (DNAK) chaperone (1-605) complexed with ADP and substrate== | ||
<StructureSection load='2kho' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2kho | <StructureSection load='2kho' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2kho]]' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2kho]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2kho]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Escherichia_coli_K-12 Escherichia coli K-12]. Full experimental information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2KHO OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2KHO FirstGlance]. <br> | ||
</td></tr><tr id=' | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">Solution NMR</td></tr> | ||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2kho FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2kho OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2kho PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2kho RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2kho PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2kho ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2kho FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2kho OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2kho PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2kho RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2kho PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2kho ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/DNAK_ECOLI DNAK_ECOLI] Plays an essential role in the initiation of phage lambda DNA replication, where it acts in an ATP-dependent fashion with the DnaJ protein to release lambda O and P proteins from the preprimosomal complex. DnaK is also involved in chromosomal DNA replication, possibly through an analogous interaction with the DnaA protein. Also participates actively in the response to hyperosmotic shock.[HAMAP-Rule:MF_00332] | |||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
[[Category: | [[Category: Escherichia coli K-12]] | ||
[[Category: Large Structures]] | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
[[Category: Bertelsen | [[Category: Bertelsen EB]] | ||
[[Category: Zuiderweg | [[Category: Zuiderweg ERP]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:38, 22 May 2024
NMR-RDC / XRAY structure of E. coli HSP70 (DNAK) chaperone (1-605) complexed with ADP and substrateNMR-RDC / XRAY structure of E. coli HSP70 (DNAK) chaperone (1-605) complexed with ADP and substrate
Structural highlights
FunctionDNAK_ECOLI Plays an essential role in the initiation of phage lambda DNA replication, where it acts in an ATP-dependent fashion with the DnaJ protein to release lambda O and P proteins from the preprimosomal complex. DnaK is also involved in chromosomal DNA replication, possibly through an analogous interaction with the DnaA protein. Also participates actively in the response to hyperosmotic shock.[HAMAP-Rule:MF_00332] Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedDnaK is the canonical Hsp70 molecular chaperone protein from Escherichia coli. Like other Hsp70s, DnaK comprises two main domains: a 44-kDa N-terminal nucleotide-binding domain (NBD) that contains ATPase activity, and a 25-kDa substrate-binding domain (SBD) that harbors the substrate-binding site. Here, we report an experimental structure for wild-type, full-length DnaK, complexed with the peptide NRLLLTG and with ADP. It was obtained in aqueous solution by using NMR residual dipolar coupling and spin labeling methods and is based on available crystal structures for the isolated NBD and SBD. By using dynamics methods, we determine that the NBD and SBD are loosely linked and can move in cones of +/-35 degrees with respect to each other. The linker region between the domains is a dynamic random coil. Nevertheless, an average structure can be defined. This structure places the SBD in close proximity of subdomain IA of the NBD and suggests that the SBD collides with the NBD at this area to establish allosteric communication. Solution conformation of wild-type E. coli Hsp70 (DnaK) chaperone complexed with ADP and substrate.,Bertelsen EB, Chang L, Gestwicki JE, Zuiderweg ER Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 May 26;106(21):8471-6. Epub 2009 May 13. PMID:19439666[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||