Bam complex: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) New page: <StructureSection load='4pk1' size='340' side='right' caption='E. coli BamA/BamB (PDB code 4pk1)' scene=''> The '''Bam''' (b-Barrel Assembly Machinery) drives the assembly of b-barrel... |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<StructureSection load='' size='340' side='right' caption='E. coli BamA barrel domain (PDB code [[4n75]])' scene='70/706705/Cv/2'> | |||
<StructureSection load=' | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
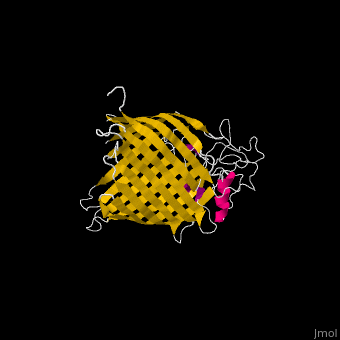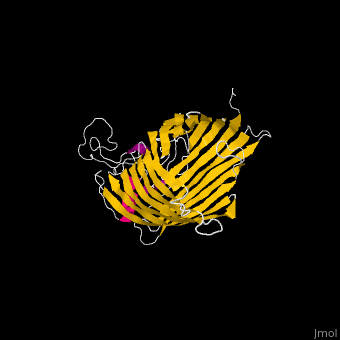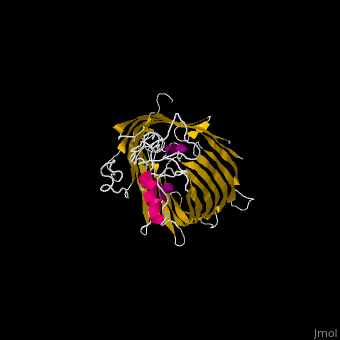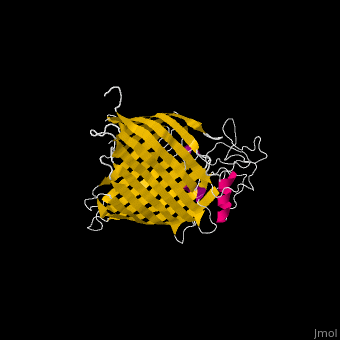
The '''Bam''' (β-Barrel Assembly Machinery) drives the assembly of β-barrel proteins into the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria.<ref>PMID:19182809</ref> | |||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
</ | The complex is composed of five subunits: '''BamA, BamB, BamC, BamD and BamE.''' Outer membrane β-barrel proteins assembly is dependent on Bam in various organisms. BamB,C,D,E bind to the N-terminal of BamA.<br /> | ||
*'''BamA''' contains five structurally homologous POTRA (POlypeptide TRAnslocation associated) domains. The POTRA domain has a β-α-α-β-β conformation. BamA barrel and at least a subset of its POTRAs are essential for viability. BamA was found also in mitochondria and chloroplasts.<br /> | |||
*'''BamD''' is composed of multiple tetratricopeptide (TPR) repeats packed into a superhelical structure. TPR is a motif containing 2 antiparallel α-helices. TPRs are found in scaffold multiprotein complexes and are involved in protein-protein interactions. | |||
== 3D Structures of Bam complex == | == 3D Structures of Bam complex == | ||
[[Bam complex 3D structures]] | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | |||
Latest revision as of 13:31, 1 April 2019
FunctionThe Bam (β-Barrel Assembly Machinery) drives the assembly of β-barrel proteins into the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria.[1] Structural highlightsThe complex is composed of five subunits: BamA, BamB, BamC, BamD and BamE. Outer membrane β-barrel proteins assembly is dependent on Bam in various organisms. BamB,C,D,E bind to the N-terminal of BamA.
3D Structures of Bam complex
|
| ||||||||||
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Knowles TJ, Scott-Tucker A, Overduin M, Henderson IR. Membrane protein architects: the role of the BAM complex in outer membrane protein assembly. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009 Mar;7(3):206-14. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2069. Epub 2009 Feb , 2. PMID:19182809 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2069