1qha: Difference between revisions
New page: left|200px <!-- The line below this paragraph, containing "STRUCTURE_1qha", creates the "Structure Box" on the page. You may change the PDB parameter (which sets the PD... |
No edit summary |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
< | ==HUMAN HEXOKINASE TYPE I COMPLEXED WITH ATP ANALOGUE AMP-PNP== | ||
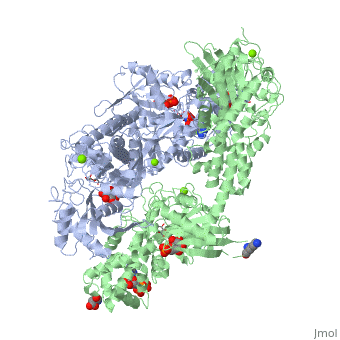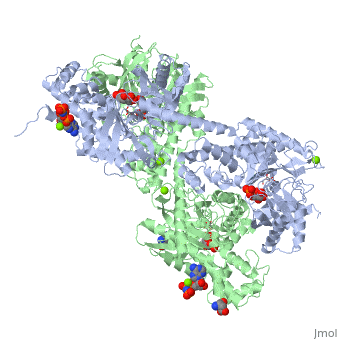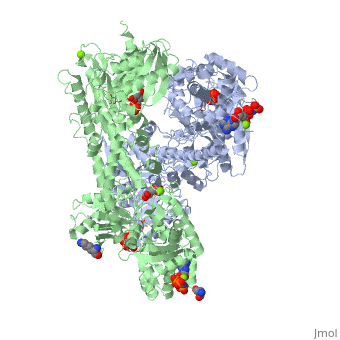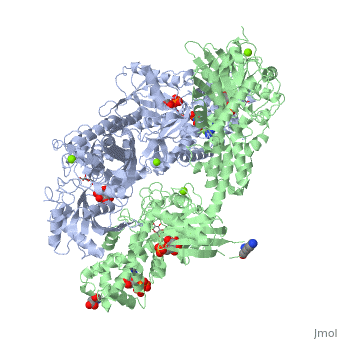
<StructureSection load='1qha' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1qha]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.25Å' scene=''> | |||
You may | == Structural highlights == | ||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1qha]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1QHA OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1QHA FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.25Å</td></tr> | |||
-- | <tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=ANP:PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC+ACID-ADENYLATE+ESTER'>ANP</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=G6P:ALPHA-D-GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE'>G6P</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=GLC:ALPHA-D-GLUCOSE'>GLC</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=MG:MAGNESIUM+ION'>MG</scene></td></tr> | ||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1qha FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1qha OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1qha PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1qha RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1qha PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1qha ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
== Disease == | |||
[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/HXK1_HUMAN HXK1_HUMAN] Defects in HK1 are the cause of hexokinase deficiency (HK deficiency) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/235700 235700]. HK deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive disease with nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia as the predominant clinical feature. | |||
== Function == | |||
[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/HXK1_HUMAN HXK1_HUMAN] | |||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | |||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | |||
Check<jmol> | |||
<jmolCheckbox> | |||
<scriptWhenChecked>; select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/qh/1qha_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | |||
<scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | |||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | |||
</jmolCheckbox> | |||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=1qha ConSurf]. | |||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
BACKGROUND: Hexokinase I sets the pace of glycolysis in the brain, catalyzing the ATP-dependent phosphorylation of glucose. The catalytic properties of hexokinase I are dependent on product inhibition as well as on the action of phosphate. In vivo, a large fraction of hexokinase I is bound to the mitochondrial outer membrane, where the enzyme adopts a tetrameric assembly. The mitochondrion-bound hexokinase I is believed to optimize the ATP/ADP exchange between glucose phosphorylation and the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation reactions. RESULTS: The crystal structure of human hexokinase I has been determined at 2.25 A resolution. The overall structure of the enzyme is in keeping with the closed conformation previously observed in yeast hexokinase. One molecule of the ATP analogue AMP-PNP is bound to each N-terminal domain of the dimeric enzyme in a surface cleft, showing specific interactions with the nucleotide, and localized positive electrostatic potential. The molecular symmetry brings the two bound AMP-PNP molecules, at the centre of two extended surface regions, to a common side of the dimeric hexokinase I molecule. CONCLUSIONS: The binding of AMP-PNP to a protein site separated from the catalytic centre of human hexokinase I can be related to the role played by some nucleotides in dissociating the enzyme from the mitochondrial membrane, and helps in defining the molecular regions of hexokinase I that are expected to be in contact with the mitochondrion. The structural information presented here is in keeping with monoclonal antibody mapping of the free and mitochondrion-bound forms of the enzyme, and with sequence analysis of hexokinases that differ in their mitochondria binding properties. | |||
Binding of non-catalytic ATP to human hexokinase I highlights the structural components for enzyme-membrane association control.,Rosano C, Sabini E, Rizzi M, Deriu D, Murshudov G, Bianchi M, Serafini G, Magnani M, Bolognesi M Structure. 1999 Nov 15;7(11):1427-37. PMID:10574795<ref>PMID:10574795</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
<div class="pdbe-citations 1qha" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | |||
== | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Hexokinase|Hexokinase]] | *[[Hexokinase|Hexokinase]] | ||
*[[Hexokinase 3D structures|Hexokinase 3D structures]] | |||
== | == References == | ||
< | <references/> | ||
__TOC__ | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
[[Category: Homo sapiens]] | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] | ||
[[Category: Bolognesi | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
[[Category: Deriu | [[Category: Bolognesi M]] | ||
[[Category: Magnani | [[Category: Deriu D]] | ||
[[Category: Rosano | [[Category: Magnani M]] | ||
[[Category: Sabini | [[Category: Rosano C]] | ||
[[Category: Sabini E]] | |||
Latest revision as of 13:02, 16 August 2023
HUMAN HEXOKINASE TYPE I COMPLEXED WITH ATP ANALOGUE AMP-PNPHUMAN HEXOKINASE TYPE I COMPLEXED WITH ATP ANALOGUE AMP-PNP
Structural highlights
DiseaseHXK1_HUMAN Defects in HK1 are the cause of hexokinase deficiency (HK deficiency) [MIM:235700. HK deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive disease with nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia as the predominant clinical feature. FunctionEvolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedBACKGROUND: Hexokinase I sets the pace of glycolysis in the brain, catalyzing the ATP-dependent phosphorylation of glucose. The catalytic properties of hexokinase I are dependent on product inhibition as well as on the action of phosphate. In vivo, a large fraction of hexokinase I is bound to the mitochondrial outer membrane, where the enzyme adopts a tetrameric assembly. The mitochondrion-bound hexokinase I is believed to optimize the ATP/ADP exchange between glucose phosphorylation and the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation reactions. RESULTS: The crystal structure of human hexokinase I has been determined at 2.25 A resolution. The overall structure of the enzyme is in keeping with the closed conformation previously observed in yeast hexokinase. One molecule of the ATP analogue AMP-PNP is bound to each N-terminal domain of the dimeric enzyme in a surface cleft, showing specific interactions with the nucleotide, and localized positive electrostatic potential. The molecular symmetry brings the two bound AMP-PNP molecules, at the centre of two extended surface regions, to a common side of the dimeric hexokinase I molecule. CONCLUSIONS: The binding of AMP-PNP to a protein site separated from the catalytic centre of human hexokinase I can be related to the role played by some nucleotides in dissociating the enzyme from the mitochondrial membrane, and helps in defining the molecular regions of hexokinase I that are expected to be in contact with the mitochondrion. The structural information presented here is in keeping with monoclonal antibody mapping of the free and mitochondrion-bound forms of the enzyme, and with sequence analysis of hexokinases that differ in their mitochondria binding properties. Binding of non-catalytic ATP to human hexokinase I highlights the structural components for enzyme-membrane association control.,Rosano C, Sabini E, Rizzi M, Deriu D, Murshudov G, Bianchi M, Serafini G, Magnani M, Bolognesi M Structure. 1999 Nov 15;7(11):1427-37. PMID:10574795[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences |
| ||||||||||||||||||