2xmx: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
< | ==High resolution structure of Colicin M== | ||
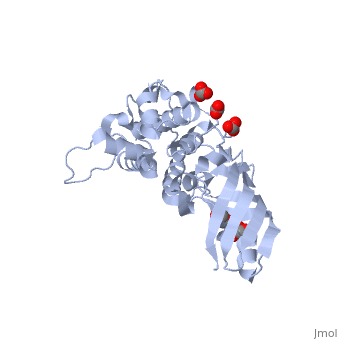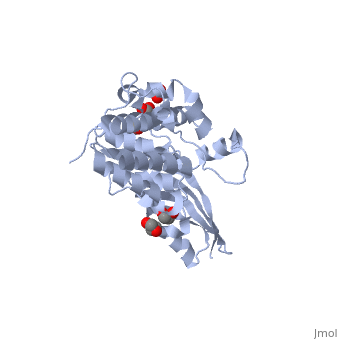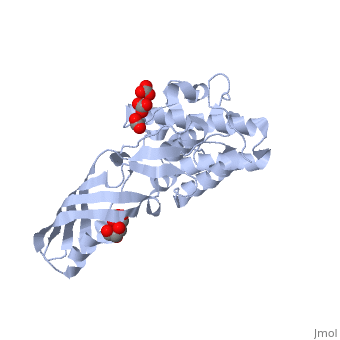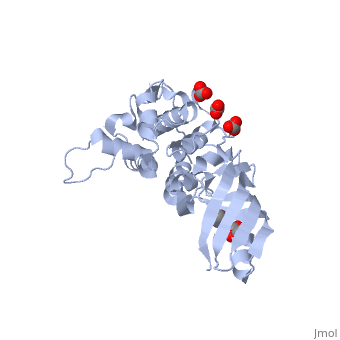
<StructureSection load='2xmx' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2xmx]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 1.67Å' scene=''> | |||
== Structural highlights == | |||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2xmx]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Escherichia_coli_K-12 Escherichia coli K-12]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2XMX OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2XMX FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 1.67Å</td></tr> | |||
-- | <tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=CO3:CARBONATE+ION'>CO3</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=GOL:GLYCEROL'>GOL</scene></td></tr> | ||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2xmx FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2xmx OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2xmx PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2xmx RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2xmx PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2xmx ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
== Function == | |||
[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CEAM_ECOLX CEAM_ECOLX] Colicins are polypeptide toxins produced by and active against E.coli and closely related bacteria. This is a calcium-requiring inhibitor for murein biosynthesis; it causes lysis of sensitive cells accompanied by murein degradation. The target site is possibly the cytoplasmic membrane. | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
Colicin M (Cma) is specifically imported into the periplasm of Escherichia coli and kills the cells. Killing depends on the periplasmic peptidyl prolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase)/chaperone FkpA. To identify the Cma prolyl bonds targeted by FkpA, we replaced the 15 proline residues individually with alanine. Nine mutant proteins were fully active; Cma(P129A), Cma(P176A), and Cma(P260A) displayed 1% and Cma(P107A) 10% of the wild-type activity. Cma(P107A), Cma(P129A), and Cma(P260A) but not Cma(P176A) killed cells after entering the periplasm via osmotic shock, indicating that the former mutants were translocation deficient; Cma(P129A) did not bind to the FhuA outer membrane receptor. The crystal structures of Cma and Cma(P176A) were identical, excluding inactivation of the activity domain located far from P176. In a new PPIase assay, FkpA isomerized the Cma prolyl bond in peptide FP(176) at a high rate but KP(107) and LP(260) at only <10% of that rate. The four mutant proteins secreted into the periplasm via a fused signal sequence were toxic but much less than wild-type Cma. Wild-type and mutant Cma proteins secreted or translocated across the outer membrane by energy-coupled import or unspecific osmotic shock were only active in the presence of FkpA. We propose that Cma unfolds during transfer across the outer or cytoplasmic membrane and refolds to the active form in the periplasm assisted by FkpA. Weak refolding of Cma(P176A) would explain its low activity in all assays. Of the four proline residues identified as being important for Cma activity, FP(176) is most likely targeted by FkpA. | |||
Activation of colicin M by the FkpA prolyl cis-trans isomerase/chaperone.,Helbig S, Patzer SI, Schiene-Fischer C, Zeth K, Braun V J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 13. PMID:21149455<ref>PMID:21149455</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
<div class="pdbe-citations 2xmx" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | |||
==See Also== | |||
*[[Colicin 3D structures|Colicin 3D structures]] | |||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
__TOC__ | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
== | [[Category: Escherichia coli K-12]] | ||
[[ | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
[[Category: Albrecht R]] | |||
== | [[Category: Braun V]] | ||
< | [[Category: Patzer SI]] | ||
[[Category: Escherichia coli | [[Category: Zeth K]] | ||
[[Category: | |||
[[Category: | |||
[[Category: | |||
[[Category: | |||
[[Category: | |||
Latest revision as of 13:34, 20 December 2023
High resolution structure of Colicin MHigh resolution structure of Colicin M
Structural highlights
FunctionCEAM_ECOLX Colicins are polypeptide toxins produced by and active against E.coli and closely related bacteria. This is a calcium-requiring inhibitor for murein biosynthesis; it causes lysis of sensitive cells accompanied by murein degradation. The target site is possibly the cytoplasmic membrane. Publication Abstract from PubMedColicin M (Cma) is specifically imported into the periplasm of Escherichia coli and kills the cells. Killing depends on the periplasmic peptidyl prolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase)/chaperone FkpA. To identify the Cma prolyl bonds targeted by FkpA, we replaced the 15 proline residues individually with alanine. Nine mutant proteins were fully active; Cma(P129A), Cma(P176A), and Cma(P260A) displayed 1% and Cma(P107A) 10% of the wild-type activity. Cma(P107A), Cma(P129A), and Cma(P260A) but not Cma(P176A) killed cells after entering the periplasm via osmotic shock, indicating that the former mutants were translocation deficient; Cma(P129A) did not bind to the FhuA outer membrane receptor. The crystal structures of Cma and Cma(P176A) were identical, excluding inactivation of the activity domain located far from P176. In a new PPIase assay, FkpA isomerized the Cma prolyl bond in peptide FP(176) at a high rate but KP(107) and LP(260) at only <10% of that rate. The four mutant proteins secreted into the periplasm via a fused signal sequence were toxic but much less than wild-type Cma. Wild-type and mutant Cma proteins secreted or translocated across the outer membrane by energy-coupled import or unspecific osmotic shock were only active in the presence of FkpA. We propose that Cma unfolds during transfer across the outer or cytoplasmic membrane and refolds to the active form in the periplasm assisted by FkpA. Weak refolding of Cma(P176A) would explain its low activity in all assays. Of the four proline residues identified as being important for Cma activity, FP(176) is most likely targeted by FkpA. Activation of colicin M by the FkpA prolyl cis-trans isomerase/chaperone.,Helbig S, Patzer SI, Schiene-Fischer C, Zeth K, Braun V J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 13. PMID:21149455[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||