Intercellular adhesion molecule: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
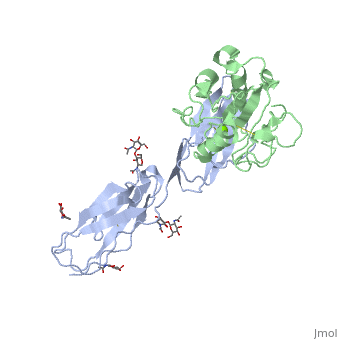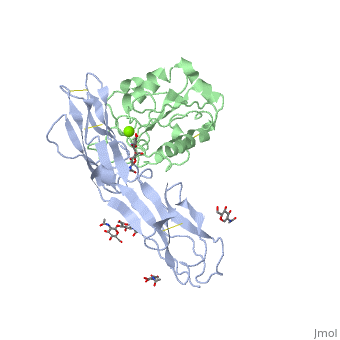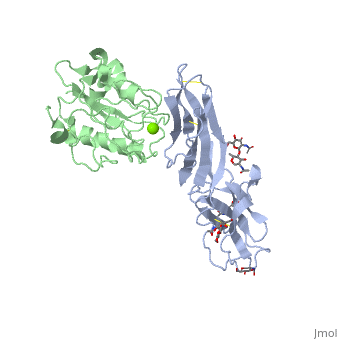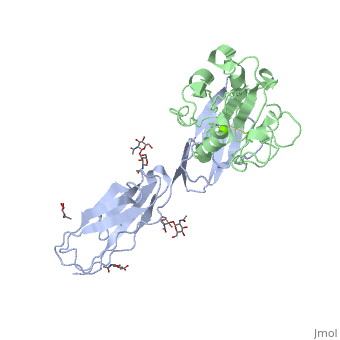
<StructureSection load='1mq8' size='340' side='right' caption='Structure of glycosylated human ICAM-1 domains 1-2 (grey | <StructureSection load='1mq8' size='340' side='right' caption='Structure of glycosylated human ICAM-1 domains 1-2 (grey) complex with LFA-1 (green) and Mg+2 ion (green) (PDB code [[1mq8]]).' scene=''> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Intercellular adhesion molecule''' (ICAM) is part of the immunoglobulin superfamily. ICAM binds to LFA-1 and macrophage-1 antigen during inflammation. ICAM contains 5 Ig-like domains. | '''Intercellular adhesion molecule''' (ICAM) is part of the immunoglobulin superfamily. ICAM binds to leukocyte function associated molecule 1 (LFA-1) and macrophage-1 antigen during inflammation<ref>PMID:8834767</ref>. ICAM contains 5 Ig-like domains. | ||
*'''ICAM-1''' is Ig-like cell adhesion molecule which has a role in inflammatory processes and in T-cell mediated host defines system. | |||
*'''ICAM-2''' mediates adhesive interactions important for antigen-specific immune response. | |||
*'''ICAM-3''' acts as recognition receptor in the phagocytosis of macrophages in engulfment of apoptotic neutrophils<ref>PMID:23775590</ref>. | |||
*'''ICAM-5''' has 2 types of binding activities: binding between neutrons and binding between neuron and leukocytes. | |||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
ICAM mutation is involved in multiple sclerosis<ref>PMID:12590979</ref>. | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 25: | Line 28: | ||
**[[1d3e]], [[1d3i]] – hICAM N terminal domain + rhinovirus coat proteins - CryoEM<br /> | **[[1d3e]], [[1d3i]] – hICAM N terminal domain + rhinovirus coat proteins - CryoEM<br /> | ||
**[[7bg7]] – hICAM + rhinovirus polyproteins - CryoEM<br /> | |||
**[[1mq8]] – hICAM domain 1-2 + LFA-1<br /> | **[[1mq8]] – hICAM domain 1-2 + LFA-1<br /> | ||
**[[3tcx]] – hICAM domain 1 + LFA-1<br /> | **[[3tcx]] – hICAM domain 1 + LFA-1<br /> | ||
**[[6eit]] – hICAM domain 1-2 + coxsakievirus coat proteins - CryoEM<br /> | |||
**[[1z7z]] – hICAM domain 1-5 + coxsakievirus coat proteins - CryoEM<br /> | **[[1z7z]] – hICAM domain 1-5 + coxsakievirus coat proteins - CryoEM<br /> | ||
**[[ | **[[2oz4]] – hICAM domain 4 + antibody<br /> | ||
**[[5mza]], [[6s8u]] – hICAM residues 28-212 + erythrocyte membrane protein 1<br /> | |||
*ICAM-2 | *ICAM-2 | ||
Latest revision as of 10:44, 4 July 2024
FunctionIntercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM) is part of the immunoglobulin superfamily. ICAM binds to leukocyte function associated molecule 1 (LFA-1) and macrophage-1 antigen during inflammation[1]. ICAM contains 5 Ig-like domains.
DiseaseICAM mutation is involved in multiple sclerosis[3].
|
| ||||||||||
3D structures of intercellular adhesion molecule3D structures of intercellular adhesion molecule
Updated on 04-July-2024
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ van de Stolpe A, van der Saag PT. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1. J Mol Med (Berl). 1996 Jan;74(1):13-33. PMID:8834767
- ↑ Kristóf E, Zahuczky G, Katona K, Doró Z, Nagy É, Fésüs L. Novel role of ICAM3 and LFA-1 in the clearance of apoptotic neutrophils by human macrophages. Apoptosis. 2013 Oct;18(10):1235-51. PMID:23775590 doi:10.1007/s10495-013-0873-z
- ↑ Nejentsev S, Laaksonen M, Tienari PJ, Fernandez O, Cordell H, Ruutiainen J, Wikstrom J, Pastinen T, Kuokkanen S, Hillert J, Ilonen J. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 K469E polymorphism: study of association with multiple sclerosis. Hum Immunol. 2003 Mar;64(3):345-9. PMID:12590979