Insulin-like growth factor receptor: Difference between revisions
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<StructureSection load='' size=' | <StructureSection load='3i81' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Human insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor complex with inhibitor (PDB code [[3i81]])'> | ||
'''Insulin-like growth factor receptors''' (IGFR) are transmembrane receptors which are stimulated by insulin-like growth factors (IGF). IGFR contains 2 extracellular α chains and 2 transmembranal β chains. Upon binding of IGF, a tyrosine in the β chain becomes autophosphorylated and triggers a cascade of intracellular signaling. | '''Insulin-like growth factor receptors''' (IGFR) are transmembrane receptors which are stimulated by insulin-like growth factors (IGF). IGFR contains 2 extracellular α chains and 2 transmembranal β chains. Upon binding of IGF, a tyrosine in the β chain becomes autophosphorylated and triggers a cascade of intracellular signaling. The insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) receptor belongs to the large class of [[Receptor tyrosine kinases|tyrosine kinase receptors]]. See also [[IGF1]], [[Growth factors]] and [[Kinase-linked, enzyme-linked and related receptors]]. | ||
*'''Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1''' is the mediator of the anabolic and mitogenic activity of growth hormone<ref>PMID: 11577173</ref><br /> | |||
*'''Insulin-like growth factor receptor 2''' is a protein hormone regulating cell proliferation, growth, migration, differentiation and survival<ref>PMID: 23257688</ref><br />. | |||
=== Memory-Enhancement by Traditional Chinese Medicine? <ref>doi 10.1080/07391102.2012.741052</ref>=== | === Memory-Enhancement by Traditional Chinese Medicine? <ref>doi 10.1080/07391102.2012.741052</ref>=== | ||
| Line 10: | Line 13: | ||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
{{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | |||
*IGFR I | |||
**[[1igr]] – hIGFR I domains 1-3 31-492– human<BR /> | |||
**[[1jqh]], [[1p4o]] - hIGFR I kinase domain (mutant) 983-1286<BR /> | |||
**[[1m7n]] - hIGFR I kinase domain<BR /> | |||
**[[1k3a]] - hIGFR I kinase domain + insulin receptor substrate peptide<BR /> | |||
**[[2oj9]], [[2zm3]], [[3d94]], [[3f5p]], [[3i81]], [[3lvp]], [[3nw5]], [[3nw6]], [[3nw7]], [[3lw0]], [[3qqu]], [[3o23]], [[4d2r]], [[5fxq]], [[5fxr]], [[5fxs]], [[5hzn]] - hIGFR I kinase domain + inhibitor<BR /> | |||
**[[5u8r]] - hIGFR I (mutant) + antibody<BR /> | |||
**[[5u8q]] - hIGFR I (mutant) + IGFI + antibody<BR /> | |||
**[[6pyh]] - hIGFR I + IGFI – Cryo EM<BR /> | |||
**[[6vwg]], [[6vwh]], [[6vwi]], [[6vwj]] - hIGFR I + IGFII – Cryo EM<BR /> | |||
**[[7s8v]] - hIGFR I + insulin receptor – Cryo EM<BR /> | |||
**[[7s0q]] - hIGFR I + insulin receptor + IGF I – Cryo EM<BR /> | |||
*IGFR II | |||
**[[1gqb]] - hIGFR II<BR /> | |||
**[[2kva]] - hIGFR II domain 5 – NMR<BR /> | |||
**[[2cnj]] - hIGFR II domain 11 - NMR<BR /> | |||
**[[2l2a]], [[2m68]], [[2m6t]] - hIGFR II domains 11 (mutant) - NMR<BR /> | |||
**[[2kvb]] - hIGFR II domain 5 + inhibitor – NMR<BR /> | |||
**[[2v5n]] - hIGFR II domains 11-12<BR /> | |||
**[[2v5o]] - hIGFR II domains 11-14<BR /> | |||
**[[2v5p]] - hIGFR II domains 11-13 + IGF II<BR /> | |||
**[[2l29]] - hIGFR II domain 11 + IGF II - NMR<BR /> | |||
**[[1gp0]], [[1gp3]], [[1e6f]] - hIGFR II IGF II-binding domain<br /> | |||
**[[1q25]] - bIGFR II domains 1-3 – bovine<BR /> | |||
**[[1syo]], [[1sz0]] - bIGFR II domains 1-3 + mannose-6-phosphate<BR /> | |||
**[[2lla]] - IGFR II domain 11 – short-beaked echidna - NMR<BR /> | |||
**[[2l2g]] - IGFR II domain 11 – opossum - NMR<BR /> | |||
}} | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:48, 3 July 2024
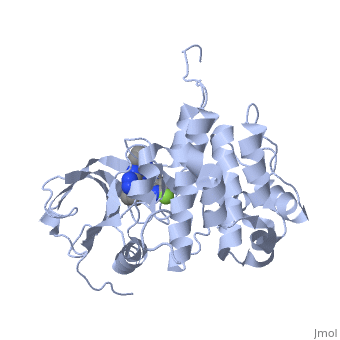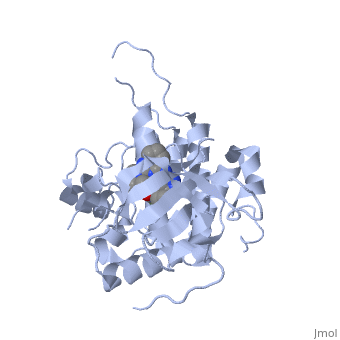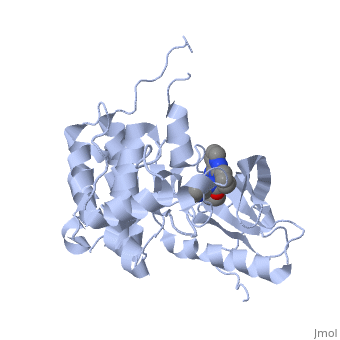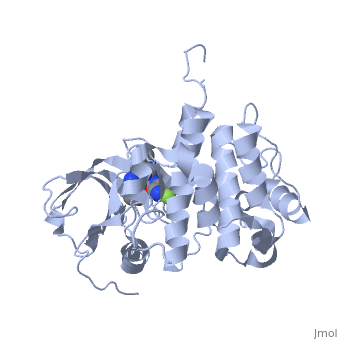
Insulin-like growth factor receptors (IGFR) are transmembrane receptors which are stimulated by insulin-like growth factors (IGF). IGFR contains 2 extracellular α chains and 2 transmembranal β chains. Upon binding of IGF, a tyrosine in the β chain becomes autophosphorylated and triggers a cascade of intracellular signaling. The insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) receptor belongs to the large class of tyrosine kinase receptors. See also IGF1, Growth factors and Kinase-linked, enzyme-linked and related receptors.
Memory-Enhancement by Traditional Chinese Medicine? [3]Cognitive impairment is an emerging issue and increasing research points to the significant role of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) in cognitive brain functions. (IGF-IR, PDB ID: 3i81, colored in darkmagenta) activation is critical for IGF-I to elicit desirable cognitive functions. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) ligands (orgin: Isatisin digotica, colored in green), (origin: Lindera aggregate, colored in deeppink), and (origin: Nelumbonucifera Gaertn, colored in salmon) showed high binding affinity towards IGF-IR at the binding site defined by the control in PDB ID: 3i81. Molecular dynamics simulation revealed that the TCM ligands were secured at the opening of the IGF-IR binding site for the duration of the MD. was stabilized by , was stabilized by , and was stabilized by (key residues are colored in yellow). Four different quantitative-structure activity relationship models consistently predicted bioactivity of the TCM ligands towards IGF-IR. In summary, the TCM candidates exhibit drug-like potential in both structural-based and ligand-based properties and may have potential for further applications in enhancing cognition. |
| ||||||||||
3D structures of insulin-like growth factor receptor3D structures of insulin-like growth factor receptor
Updated on 03-July-2024
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Laron Z. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1): a growth hormone. Mol Pathol. 2001 Oct;54(5):311-6. PMID:11577173
- ↑ Bergman D, Halje M, Nordin M, Engström W. Insulin-like growth factor 2 in development and disease: a mini-review. Gerontology. 2013;59(3):240-9. PMID:23257688 doi:10.1159/000343995
- ↑ Hung IC, Chang SS, Chang PC, Lee CC, Chen CY. Memory enhancement by traditional Chinese medicine? J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2012 Dec 19. PMID:23249175 doi:10.1080/07391102.2012.741052