2vaa: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==MHC CLASS I H-2KB HEAVY CHAIN COMPLEXED WITH BETA-2 MICROGLOBULIN AND VESICULAR STOMATITIS VIRUS NUCLEOPROTEIN== | |||
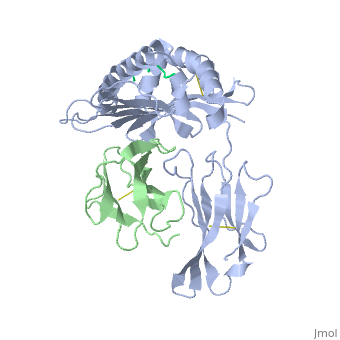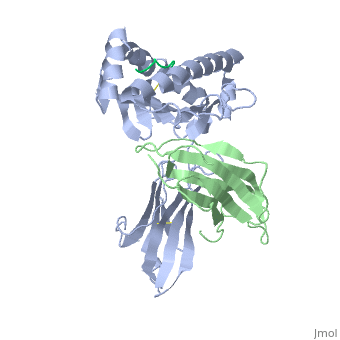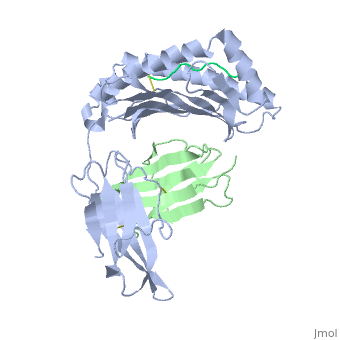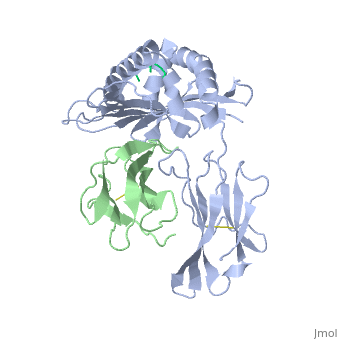
<StructureSection load='2vaa' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2vaa]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.30Å' scene=''> | |||
== Structural highlights == | |||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2vaa]] is a 3 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mus_musculus Mus musculus] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vesicular_stomatitis_virus Vesicular stomatitis virus]. This structure supersedes the now removed PDB entry [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/send-pdb?obs=1&id=1vaa 1vaa]. The February 2005 RCSB PDB [https://pdb.rcsb.org/pdb/static.do?p=education_discussion/molecule_of_the_month/index.html Molecule of the Month] feature on ''Major Histocompatibility Complex'' by David S. Goodsell is [https://dx.doi.org/10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2005_2 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2005_2]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2VAA OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2VAA FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.3Å</td></tr> | |||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2vaa FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2vaa OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2vaa PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2vaa RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2vaa PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2vaa ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
== Function == | |||
[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/HA1B_MOUSE HA1B_MOUSE] Involved in the presentation of foreign antigens to the immune system. | |||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | |||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | |||
Check<jmol> | |||
<jmolCheckbox> | |||
<scriptWhenChecked>; select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/va/2vaa_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | |||
<scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | |||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | |||
</jmolCheckbox> | |||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=2vaa ConSurf]. | |||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
The x-ray structures of a murine MHC class I molecule (H-2Kb) were determined in complex with two different viral peptides, derived from the vesicular stomatitis virus nucleoprotein (52-59), VSV-8, and the Sendai virus nucleoprotein (324-332), SEV-9. The H-2Kb complexes were refined at 2.3 A for VSV-8 and 2.5 A for SEV-9. The structure of H-2Kb exhibits a high degree of similarity with human HLA class I, although the individual domains can have slightly altered dispositions. Both peptides bind in extended conformations with most of their surfaces buried in the H-2Kb binding groove. The nonamer peptide maintains the same amino- and carboxyl-terminal interactions as the octamer primarily by the insertion of a bulge in the center of an otherwise beta conformation. Most of the specific interactions are between side-chain atoms of H-2Kb and main-chain atoms of peptide. This binding scheme accounts in large part for the enormous diversity of peptide sequences that bind with high affinity to class I molecules. Small but significant conformational changes in H-2Kb are associated with peptide binding, and these synergistic movements may be an integral part of the T cell receptor recognition process. | |||
Crystal structures of two viral peptides in complex with murine MHC class I H-2Kb.,Fremont DH, Matsumura M, Stura EA, Peterson PA, Wilson IA Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):919-27. PMID:1323877<ref>PMID:1323877</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
<div class="pdbe-citations 2vaa" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Beta-2 microglobulin|Beta-2 microglobulin]] | *[[Beta-2 microglobulin 3D structures|Beta-2 microglobulin 3D structures]] | ||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
__TOC__ | |||
== | </StructureSection> | ||
< | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
[[Category: Major Histocompatibility Complex]] | [[Category: Major Histocompatibility Complex]] | ||
[[Category: Mus musculus]] | [[Category: Mus musculus]] | ||
[[Category: RCSB PDB Molecule of the Month]] | [[Category: RCSB PDB Molecule of the Month]] | ||
[[Category: Vesicular stomatitis virus]] | [[Category: Vesicular stomatitis virus]] | ||
[[Category: Fremont | [[Category: Fremont DH]] | ||
[[Category: Wilson | [[Category: Wilson IA]] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:39, 5 June 2024
MHC CLASS I H-2KB HEAVY CHAIN COMPLEXED WITH BETA-2 MICROGLOBULIN AND VESICULAR STOMATITIS VIRUS NUCLEOPROTEINMHC CLASS I H-2KB HEAVY CHAIN COMPLEXED WITH BETA-2 MICROGLOBULIN AND VESICULAR STOMATITIS VIRUS NUCLEOPROTEIN
Structural highlights
FunctionHA1B_MOUSE Involved in the presentation of foreign antigens to the immune system. Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedThe x-ray structures of a murine MHC class I molecule (H-2Kb) were determined in complex with two different viral peptides, derived from the vesicular stomatitis virus nucleoprotein (52-59), VSV-8, and the Sendai virus nucleoprotein (324-332), SEV-9. The H-2Kb complexes were refined at 2.3 A for VSV-8 and 2.5 A for SEV-9. The structure of H-2Kb exhibits a high degree of similarity with human HLA class I, although the individual domains can have slightly altered dispositions. Both peptides bind in extended conformations with most of their surfaces buried in the H-2Kb binding groove. The nonamer peptide maintains the same amino- and carboxyl-terminal interactions as the octamer primarily by the insertion of a bulge in the center of an otherwise beta conformation. Most of the specific interactions are between side-chain atoms of H-2Kb and main-chain atoms of peptide. This binding scheme accounts in large part for the enormous diversity of peptide sequences that bind with high affinity to class I molecules. Small but significant conformational changes in H-2Kb are associated with peptide binding, and these synergistic movements may be an integral part of the T cell receptor recognition process. Crystal structures of two viral peptides in complex with murine MHC class I H-2Kb.,Fremont DH, Matsumura M, Stura EA, Peterson PA, Wilson IA Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):919-27. PMID:1323877[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences |
| ||||||||||||||||