Estrogen receptor: Difference between revisions
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (33 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
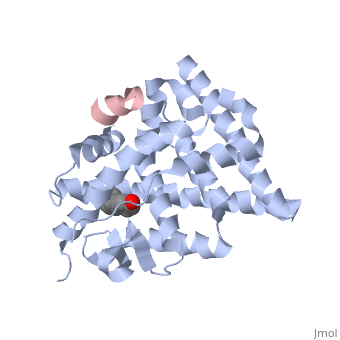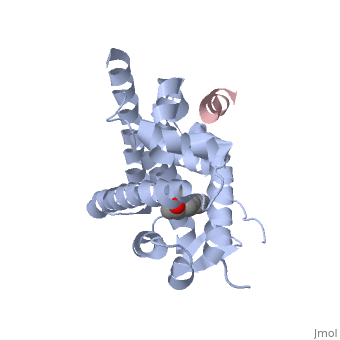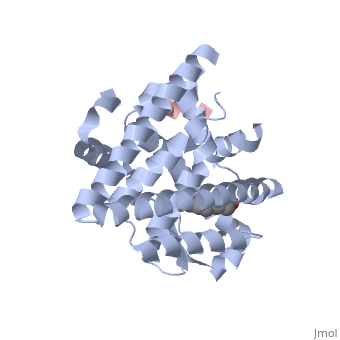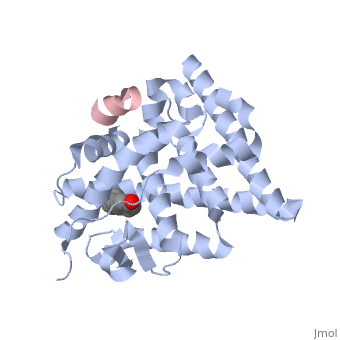
<StructureSection load='1gwr' size=' | <StructureSection load='1gwr' size='275' side='right' scene='' caption='Human estrogen receptor-ligand binding domain (grey) complex with transcription intermediate factor-2 peptide (pink) and estradiol (PDB code [[1gwr]])'> | ||
[[Image:2yat.png|left|200px|thumb|Crystal structure of estradiol derived metal chelate and estrogen receptor-ligand binding domain complex [[2yat]]]] | [[Image:2yat.png|left|200px|thumb|Crystal structure of estradiol derived metal chelate and estrogen receptor-ligand binding domain complex '''[[2yat]]''']] | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
__TOC__ | |||
==Estrogen receptors== | |||
(ER) are activated by the hormone estrogen (EST). It is a [[Nuclear receptors|nuclear receptor]]. The activated ER binds DNA and regulates the activity of many genes. There are 2 forms of ER: α and β and ER dimers can be of αα, ββ and αβ. The 2 forms differ in the tissues in which they are found. ER is composed of 5 domains: N terminal A/B domain can transactivate transcription without binding estrogen; C domain (DBD) binds to Estrogen response elements of DNA; D domain is a hinge region; E domain is ligand binding (LBD) as well as binding the coactivator and corepressor proteins and transactivates gene transcription.<br /> | |||
See also [[Intracellular receptors]] | |||
==Structure of estradiol metal chelate and estrogen receptor complex: The basis for designing a new class of SERMs <ref>PMID: 21473635</ref>== | |||
Selective estrogen receptor modulators, such as estradiol 17-derived metal complexes, have been synthesized as targeted probes for the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer. Here, we report the detailed 3D structure of <scene name='Journal:JMEDCHEM:1/Cv/11'>estrogen receptor alpha ligand-binding domain (ER-LBD)</scene> bound with a novel <scene name='Journal:JMEDCHEM:1/Cv/5'>estradiol-derived metal complex, estradiol-pyridinium tetra acetate europium (III) (EPTA-Eu)</scene> at 2.6Å resolution (PDB ID '''[[2yat]]'''). The residues <scene name='Journal:JMEDCHEM:1/Cv/10'>Glu353, Arg394 and His524 and the conserved water molecule (W1006) form hydrogen bonds</scene> with EPTA-Eu. The hydrogen bonds are shown as white dashed lines. <scene name='Journal:JMEDCHEM:1/Cv/7'>Superposition</scene> of this structure with the structure of native ligand 17β-estradiol (E2) in the complex of E2/ERα-LBD complex ('''[[1ere]]''') reveals that the <scene name='Journal:JMEDCHEM:1/Cv/12'>E2 core of EPTA-Eu overlaps closely with that of E2 itself</scene>. The <scene name='Journal:JMEDCHEM:1/Cv/9'>hydrogen bonds network</scene> made by additional estrogen receptor residues (''e.g.'' Glu419 of H7 and Glu339 of H3, this depends on subunit), may work together with the E2 17β hydroxyl-His524 hydrogen bond and tighten the neck of the LBP upon binding of the endogenous ligand E2. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen (OHT) is an other selective estrogen receptor modulator. <scene name='Journal:JMEDCHEM:1/Al/5'>Superposition</scene> of EPTA-Eu/ERα-LBD complex on OHT/ERα-LBD complex ('''[[3ert]]''') shows that there is similar network of hydrogen bonds in both complexes, except for His524 which does not form hydrogen bond with OHT in the OHT/ERα-LBD complex. <scene name='Journal:JMEDCHEM:1/Al1/3'>Superposition of structures of all these three complexes:</scene> E2/ERα-LBD ('''[[1ere]]'''), OHT/ERα-LBD ('''[[3ert]]''') and EPTA-Eu/ERα-LBD shows that they overlap well in the majority portions of the domain, but differ significantly in the region of the 'omega loop'. They display different synergistic reciprocating movements, depending on the specific nature of the ligand bound. The structure of estrogen receptor complexed with EPTA-Eu provides important information pertinent to the design of novel functional ER targeted probes for clinical applications. | |||
==Estrogen receptor α complexed with raloxifene and a corepressor peptide== | |||
<scene name='Estrogen_receptor/Cv/1'>Click here to see the difference between conformations</scene> of estrogen receptor α complexed with its modulator [[Raloxifene]] and a corepressor peptide (morph was taken from [http://molmovdb.org/cgi-bin/movie.cgi Gallery of Morphs] of the [http://molmovdb.org Yale Morph Server]). | |||
<scene name='Estrogen_receptor/Cv/1'>Click here to see the difference between conformations</scene> of estrogen receptor α complexed with | |||
==3D structures of estrogen receptor== | ==3D structures of estrogen receptor== | ||
[[Estrogen receptor 3D structures]] | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
__NOTOC__ | |||
==For more details see== | |||
[[Hormone]]<br /> | |||
[[Ivan Koutsopatriy estrogen receptor]]<br /> | |||
[[C-di-GMP receptors with PilZ domain]]<br /> | |||
[[Estrogens]]<br /> | |||
For more details on ERβ see [[Student Project 10 for UMass Chemistry 423 Spring 2015]]<br /> | |||
For more details on ER-Tamoxifen complex see [[Tamoxifen]]. | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
'''Reference''' | '''Reference''' | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
[[Category:Hormone]] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:05, 19 June 2024
 Estrogen receptors(ER) are activated by the hormone estrogen (EST). It is a nuclear receptor. The activated ER binds DNA and regulates the activity of many genes. There are 2 forms of ER: α and β and ER dimers can be of αα, ββ and αβ. The 2 forms differ in the tissues in which they are found. ER is composed of 5 domains: N terminal A/B domain can transactivate transcription without binding estrogen; C domain (DBD) binds to Estrogen response elements of DNA; D domain is a hinge region; E domain is ligand binding (LBD) as well as binding the coactivator and corepressor proteins and transactivates gene transcription. See also Intracellular receptors Structure of estradiol metal chelate and estrogen receptor complex: The basis for designing a new class of SERMs [1]Selective estrogen receptor modulators, such as estradiol 17-derived metal complexes, have been synthesized as targeted probes for the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer. Here, we report the detailed 3D structure of bound with a novel at 2.6Å resolution (PDB ID 2yat). The residues with EPTA-Eu. The hydrogen bonds are shown as white dashed lines. of this structure with the structure of native ligand 17β-estradiol (E2) in the complex of E2/ERα-LBD complex (1ere) reveals that the . The made by additional estrogen receptor residues (e.g. Glu419 of H7 and Glu339 of H3, this depends on subunit), may work together with the E2 17β hydroxyl-His524 hydrogen bond and tighten the neck of the LBP upon binding of the endogenous ligand E2. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen (OHT) is an other selective estrogen receptor modulator. of EPTA-Eu/ERα-LBD complex on OHT/ERα-LBD complex (3ert) shows that there is similar network of hydrogen bonds in both complexes, except for His524 which does not form hydrogen bond with OHT in the OHT/ERα-LBD complex. E2/ERα-LBD (1ere), OHT/ERα-LBD (3ert) and EPTA-Eu/ERα-LBD shows that they overlap well in the majority portions of the domain, but differ significantly in the region of the 'omega loop'. They display different synergistic reciprocating movements, depending on the specific nature of the ligand bound. The structure of estrogen receptor complexed with EPTA-Eu provides important information pertinent to the design of novel functional ER targeted probes for clinical applications. Estrogen receptor α complexed with raloxifene and a corepressor peptideof estrogen receptor α complexed with its modulator Raloxifene and a corepressor peptide (morph was taken from Gallery of Morphs of the Yale Morph Server). 3D structures of estrogen receptorEstrogen receptor 3D structures
|
| ||||||||||
For more details seeFor more details see
Hormone
Ivan Koutsopatriy estrogen receptor
C-di-GMP receptors with PilZ domain
Estrogens
For more details on ERβ see Student Project 10 for UMass Chemistry 423 Spring 2015
For more details on ER-Tamoxifen complex see Tamoxifen.
Reference
- ↑ Li MJ, Greenblatt HM, Dym O, Albeck S, Pais A, Gunanathan C, Milstein D, Degani H, Sussman JL. Structure of estradiol metal chelate and estrogen receptor complex: The basis for designing a new class of selective estrogen receptor modulators. J Med Chem. 2011 Apr 7. PMID:21473635 doi:10.1021/jm200192y