Sodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory factor: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
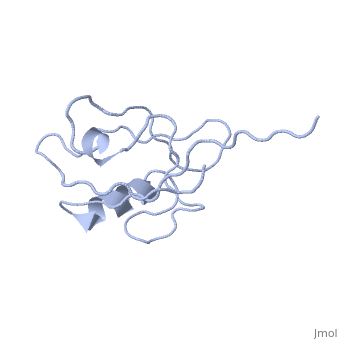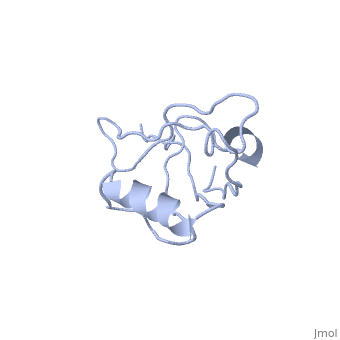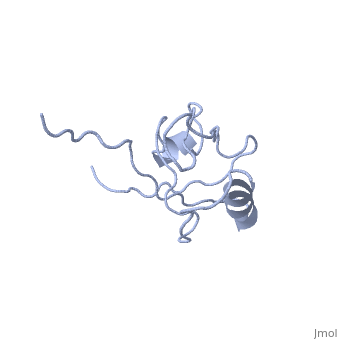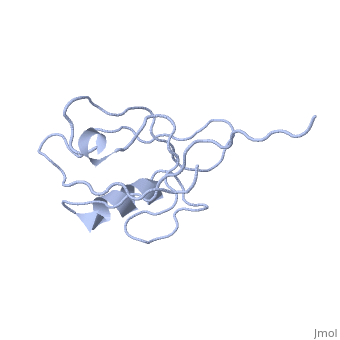
<StructureSection load='' size='340' side='right' caption='Human NHERF-1 second PDZ domain with CXCR2 peptide chimera (PDB cod [[4q3h]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='4q3h' size='340' side='right' caption='Human NHERF-1 second PDZ domain with CXCR2 peptide chimera (PDB cod [[4q3h]])' scene=''> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Sodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory factors''' (NHERF) are multifunctional adaptor protein which plays a role in the assembly of signal transduction complexes, linking ion channels and receptors to the actin skeleton<ref>PMID:11141479</ref>. | '''Sodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory factors''' (NHERF) or '''ezrin-radixin-moesin binding phosphoprotein-50''' or '''PDZ domain-containing protein''' or '''Na+/H+ exchange regulatory cofactor NHE-RF1''' or '''NHERF''' are multifunctional adaptor protein which plays a role in the assembly of signal transduction complexes, linking ion channels and receptors to the actin skeleton<ref>PMID:11141479</ref>. | ||
* '''NHERF-1''' is the major isoform present in the brain and it regulates the trans-cellular ion transport through the blood-brain barrier membrane<ref>PMID:26010555</ref>. It transduces cyclic AMP signals that inhibit the sodium-hydrogen exchanger present at the surface of kidney and gut<ref>PMID:12586353</ref>. NHERF-1 contains 2 PDZ domains and one erm domain. | |||
* '''NHERF-2''' is a negative regulator of endothelial proliferation and may have important roles in endothelial homeostasis and vascular modeling<ref>PMID:22343917</ref>. NHERF-2 contains 2 PDZ domains and one erm domain. | |||
*'''NHERF-3''' contains 4 PDZ domains no erm domain<ref>PMID:15905209</ref>. | |||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| Line 14: | Line 17: | ||
NHERF interacts with ion transporters and receptors via its PDZ domains and with the merlin, ezrin, radixin and moesin proteins via its c-terminal. The CXCR2 peptide binds the second PDZ domain hydrophobic cleft<ref>PMID:26010555</ref>. | NHERF interacts with ion transporters and receptors via its PDZ domains and with the merlin, ezrin, radixin and moesin proteins via its c-terminal. The CXCR2 peptide binds the second PDZ domain hydrophobic cleft<ref>PMID:26010555</ref>. | ||
== 3D Structures of sodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory factor == | == 3D Structures of sodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory factor == | ||
[[Sodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory factor 3D structures]] | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
</StructureSection> | |||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:16, 13 August 2024
FunctionSodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory factors (NHERF) or ezrin-radixin-moesin binding phosphoprotein-50 or PDZ domain-containing protein or Na+/H+ exchange regulatory cofactor NHE-RF1 or NHERF are multifunctional adaptor protein which plays a role in the assembly of signal transduction complexes, linking ion channels and receptors to the actin skeleton[1].
RelevanceNHERF-1 inhibitors represent a potentially effective therapeutic approach to the treatment of hear failure[6]. NHERF-1 has a vital role in kidney cell survival[7]. NHERF are known to be involved in pathophysiologies of many brain diseases like epilepsy, Alzhheimer's disease, neuropathic pain and stroke. Structural highlightsNHERF interacts with ion transporters and receptors via its PDZ domains and with the merlin, ezrin, radixin and moesin proteins via its c-terminal. The CXCR2 peptide binds the second PDZ domain hydrophobic cleft[8]. 3D Structures of sodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory factorSodium-hydrogen exchange regulatory factor 3D structures References
|
| ||||||||||