1bg1: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
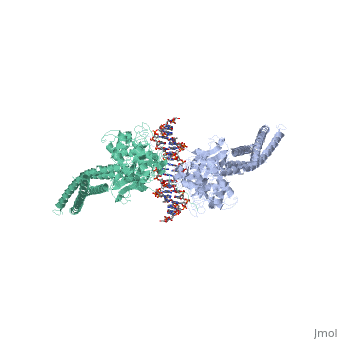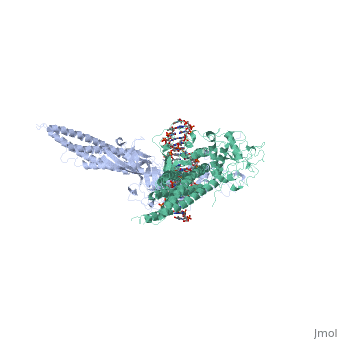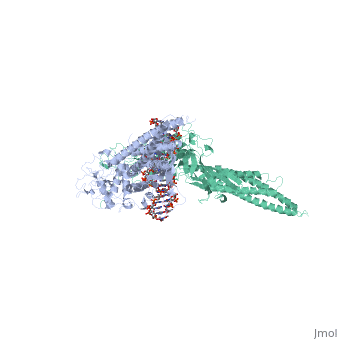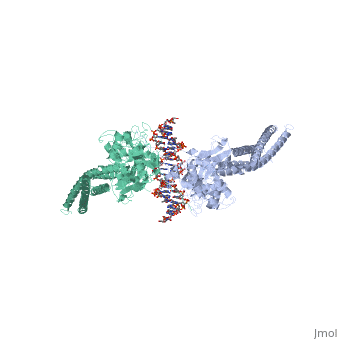
< | ==TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR STAT3B/DNA COMPLEX== | ||
<StructureSection load='1bg1' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1bg1]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.25Å' scene=''> | |||
== Structural highlights == | |||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1bg1]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mus_musculus Mus musculus]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1BG1 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1BG1 FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.25Å</td></tr> | |||
- | <tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=PTR:O-PHOSPHOTYROSINE'>PTR</scene></td></tr> | ||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1bg1 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1bg1 OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1bg1 PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1bg1 RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1bg1 PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1bg1 ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
== Function == | |||
[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/STAT3_MOUSE STAT3_MOUSE] Signal transducer and transcription activator that mediates cellular responses to interleukins, KITLG/SCF and other growth factors. May mediate cellular responses to activated FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3 and FGFR4. Binds to the interleukin-6 (IL-6)-responsive elements identified in the promoters of various acute-phase protein genes. Activated by IL31 through IL31RA. STAT3B interacts with the N-terminal part of JUN to activate such promoters in a cooperative way.<ref>PMID:11294897</ref> | |||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | |||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | |||
Check<jmol> | |||
<jmolCheckbox> | |||
<scriptWhenChecked>; select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/bg/1bg1_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | |||
<scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview03.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | |||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | |||
</jmolCheckbox> | |||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=1bg1 ConSurf]. | |||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
STAT proteins are a family of eukaryotic transcription factors that mediate the response to a large number of cytokines and growth factors. Upon activation by cell-surface receptors or their associated kinases, STAT proteins dimerize, translocate to the nucleus and bind to specific promoter sequences on their target genes. Here we report the first crystal structure of a STAT protein bound to its DNA recognition site at 2.25 A resolution. The structure provides insight into the various steps by which STAT proteins deliver a response signal directly from the cell membrane to their target genes in the nucleus. | |||
Three-dimensional structure of the Stat3beta homodimer bound to DNA.,Becker S, Groner B, Muller CW Nature. 1998 Jul 9;394(6689):145-51. PMID:9671298<ref>PMID:9671298</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
<div class="pdbe-citations 1bg1" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | |||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
__TOC__ | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
== | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
== | |||
< | |||
[[Category: Mus musculus]] | [[Category: Mus musculus]] | ||
[[Category: Becker | [[Category: Becker S]] | ||
[[Category: Groner | [[Category: Groner B]] | ||
[[Category: Muller | [[Category: Muller CW]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:25, 30 October 2024
TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR STAT3B/DNA COMPLEXTRANSCRIPTION FACTOR STAT3B/DNA COMPLEX
Structural highlights
FunctionSTAT3_MOUSE Signal transducer and transcription activator that mediates cellular responses to interleukins, KITLG/SCF and other growth factors. May mediate cellular responses to activated FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3 and FGFR4. Binds to the interleukin-6 (IL-6)-responsive elements identified in the promoters of various acute-phase protein genes. Activated by IL31 through IL31RA. STAT3B interacts with the N-terminal part of JUN to activate such promoters in a cooperative way.[1] Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedSTAT proteins are a family of eukaryotic transcription factors that mediate the response to a large number of cytokines and growth factors. Upon activation by cell-surface receptors or their associated kinases, STAT proteins dimerize, translocate to the nucleus and bind to specific promoter sequences on their target genes. Here we report the first crystal structure of a STAT protein bound to its DNA recognition site at 2.25 A resolution. The structure provides insight into the various steps by which STAT proteins deliver a response signal directly from the cell membrane to their target genes in the nucleus. Three-dimensional structure of the Stat3beta homodimer bound to DNA.,Becker S, Groner B, Muller CW Nature. 1998 Jul 9;394(6689):145-51. PMID:9671298[2] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. References
|
| ||||||||||||||||||