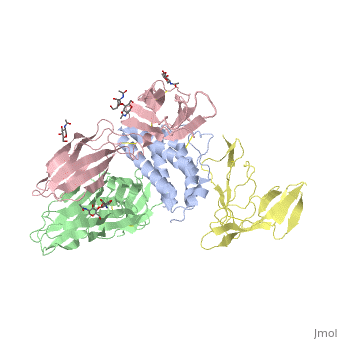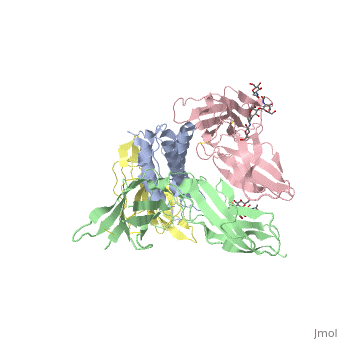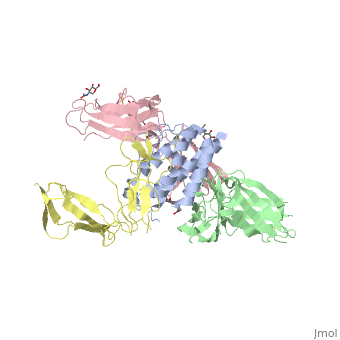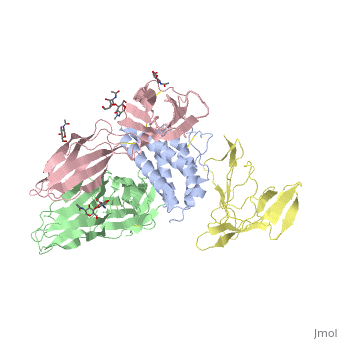2b5i: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
< | ==cytokine receptor complex== | ||
<StructureSection load='2b5i' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2b5i]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.30Å' scene=''> | |||
You may | == Structural highlights == | ||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2b5i]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2B5I OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2B5I FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.3Å</td></tr> | |||
-- | <tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=NAG:N-ACETYL-D-GLUCOSAMINE'>NAG</scene></td></tr> | ||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2b5i FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2b5i OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2b5i PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2b5i RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2b5i PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2b5i ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
== Function == | |||
[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/IL2RB_HUMAN IL2RB_HUMAN] Receptor for interleukin-2. This beta subunit is involved in receptor mediated endocytosis and transduces the mitogenic signals of IL2. | |||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | |||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | |||
Check<jmol> | |||
<jmolCheckbox> | |||
<scriptWhenChecked>; select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/b5/2b5i_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | |||
<scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview03.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | |||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | |||
</jmolCheckbox> | |||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=2b5i ConSurf]. | |||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is an immunoregulatory cytokine that acts through a quaternary receptor signaling complex containing alpha (IL-2Ralpha), beta (IL-2Rbeta), and common gamma chain (gc) receptors. In the structure of the quaternary ectodomain complex as visualized at a resolution of 2.3 angstroms, the binding of IL-2Ralpha to IL-2 stabilizes a secondary binding site for presentation to IL-2Rbeta. gammac is then recruited to the composite surface formed by the IL-2/IL-2Rbeta complex. Consistent with its role as a shared receptor for IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21, gammac forms degenerate contacts with IL-2. The structure of gammac provides a rationale for loss-of-function mutations found in patients with X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency diseases (X-SCID). This complex structure provides a framework for other gammac-dependent cytokine-receptor interactions and for the engineering of improved IL-2 therapeutics. | |||
Structure of the quaternary complex of interleukin-2 with its alpha, beta, and gammac receptors.,Wang X, Rickert M, Garcia KC Science. 2005 Nov 18;310(5751):1159-63. PMID:16293754<ref>PMID:16293754</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
<div class="pdbe-citations 2b5i" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | |||
==See Also== | |||
*[[Interleukin 3D structures|Interleukin 3D structures]] | |||
*[[Interleukin receptor|Interleukin receptor]] | |||
*[[Interleukin receptor 3D structures|Interleukin receptor 3D structures]] | |||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
== | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | |||
== | |||
[[Category: Homo sapiens]] | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category: Garcia KC]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category: Rickert M]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category: Wang X]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:00, 6 November 2024
cytokine receptor complexcytokine receptor complex
Structural highlights
FunctionIL2RB_HUMAN Receptor for interleukin-2. This beta subunit is involved in receptor mediated endocytosis and transduces the mitogenic signals of IL2. Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedInterleukin-2 (IL-2) is an immunoregulatory cytokine that acts through a quaternary receptor signaling complex containing alpha (IL-2Ralpha), beta (IL-2Rbeta), and common gamma chain (gc) receptors. In the structure of the quaternary ectodomain complex as visualized at a resolution of 2.3 angstroms, the binding of IL-2Ralpha to IL-2 stabilizes a secondary binding site for presentation to IL-2Rbeta. gammac is then recruited to the composite surface formed by the IL-2/IL-2Rbeta complex. Consistent with its role as a shared receptor for IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21, gammac forms degenerate contacts with IL-2. The structure of gammac provides a rationale for loss-of-function mutations found in patients with X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency diseases (X-SCID). This complex structure provides a framework for other gammac-dependent cytokine-receptor interactions and for the engineering of improved IL-2 therapeutics. Structure of the quaternary complex of interleukin-2 with its alpha, beta, and gammac receptors.,Wang X, Rickert M, Garcia KC Science. 2005 Nov 18;310(5751):1159-63. PMID:16293754[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||