2clt: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
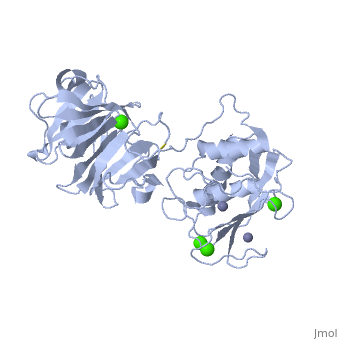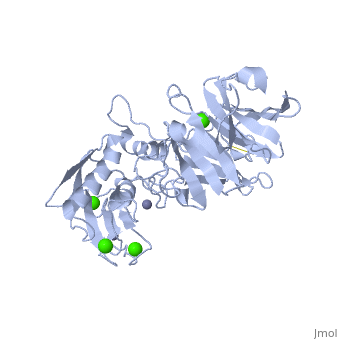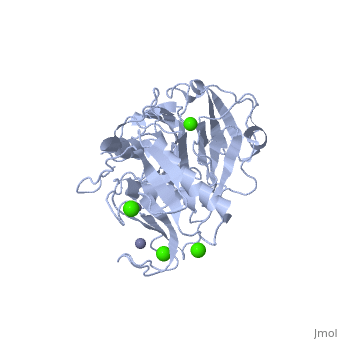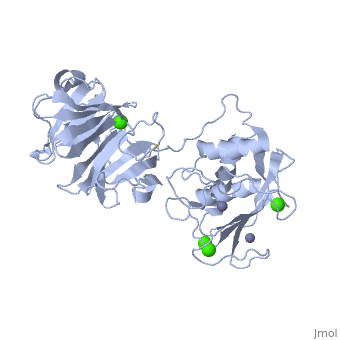
==Crystal structure of the active form (full-length) of human fibroblast collagenase.== | |||
<StructureSection load='2clt' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2clt]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.67Å' scene=''> | |||
== Structural highlights == | |||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2clt]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2CLT OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2CLT FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.67Å</td></tr> | |||
<tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=CA:CALCIUM+ION'>CA</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=ZN:ZINC+ION'>ZN</scene></td></tr> | |||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2clt FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2clt OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2clt PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2clt RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2clt PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2clt ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
== Function == | |||
[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/MMP1_HUMAN MMP1_HUMAN] Cleaves collagens of types I, II, and III at one site in the helical domain. Also cleaves collagens of types VII and X. In case of HIV infection, interacts and cleaves the secreted viral Tat protein, leading to a decrease in neuronal Tat's mediated neurotoxicity.<ref>PMID:1645757</ref> | |||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | |||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | |||
Check<jmol> | |||
<jmolCheckbox> | |||
<scriptWhenChecked>; select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/cl/2clt_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | |||
<scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview03.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | |||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | |||
</jmolCheckbox> | |||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=2clt ConSurf]. | |||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
The extracellular matrix is a dynamic environment that constantly undergoes remodelling and degradation during vital physiological processes such as angiogenesis, wound healing, and development. Unbalanced extracellular matrix breakdown is associated with many diseases such as arthritis, cancer and fibrosis. Interstitial collagen is degraded by matrix metalloproteinases with collagenolytic activity by MMP-1, MMP-8 and MMP-13, collectively known as the collagenases. Matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP-1) plays a pivotal role in degradation of interstitial collagen types I, II, and III. Here, we report the crystal structure of the active form of human MMP-1 at 2.67 A resolution. This is the first MMP-1 structure that is free of inhibitor and a water molecule essential for peptide hydrolysis is observed coordinated with the active site zinc. Comparing this structure with the human proMMP-1 shows significant structural differences, mainly in the relative orientation of the hemopexin domain, between the pro form and active form of the human enzyme. | |||
Crystal structure of an active form of human MMP-1.,Iyer S, Visse R, Nagase H, Acharya KR J Mol Biol. 2006 Sep 8;362(1):78-88. Epub 2006 Aug 4. PMID:16890240<ref>PMID:16890240</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
<div class="pdbe-citations 2clt" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | |||
== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Matrix metalloproteinase 3D structures|Matrix metalloproteinase 3D structures]] | |||
== References == | |||
== | <references/> | ||
__TOC__ | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
[[Category: Homo sapiens]] | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
[[Category: Acharya KR]] | |||
[[Category: Acharya | [[Category: Iyer S]] | ||
[[Category: Iyer | [[Category: Nagase H]] | ||
[[Category: Nagase | [[Category: Visse R]] | ||
[[Category: Visse | |||
Latest revision as of 12:04, 6 November 2024
Crystal structure of the active form (full-length) of human fibroblast collagenase.Crystal structure of the active form (full-length) of human fibroblast collagenase.
Structural highlights
FunctionMMP1_HUMAN Cleaves collagens of types I, II, and III at one site in the helical domain. Also cleaves collagens of types VII and X. In case of HIV infection, interacts and cleaves the secreted viral Tat protein, leading to a decrease in neuronal Tat's mediated neurotoxicity.[1] Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedThe extracellular matrix is a dynamic environment that constantly undergoes remodelling and degradation during vital physiological processes such as angiogenesis, wound healing, and development. Unbalanced extracellular matrix breakdown is associated with many diseases such as arthritis, cancer and fibrosis. Interstitial collagen is degraded by matrix metalloproteinases with collagenolytic activity by MMP-1, MMP-8 and MMP-13, collectively known as the collagenases. Matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP-1) plays a pivotal role in degradation of interstitial collagen types I, II, and III. Here, we report the crystal structure of the active form of human MMP-1 at 2.67 A resolution. This is the first MMP-1 structure that is free of inhibitor and a water molecule essential for peptide hydrolysis is observed coordinated with the active site zinc. Comparing this structure with the human proMMP-1 shows significant structural differences, mainly in the relative orientation of the hemopexin domain, between the pro form and active form of the human enzyme. Crystal structure of an active form of human MMP-1.,Iyer S, Visse R, Nagase H, Acharya KR J Mol Biol. 2006 Sep 8;362(1):78-88. Epub 2006 Aug 4. PMID:16890240[2] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||