1cfc: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | ==CALCIUM-FREE CALMODULIN== | ||
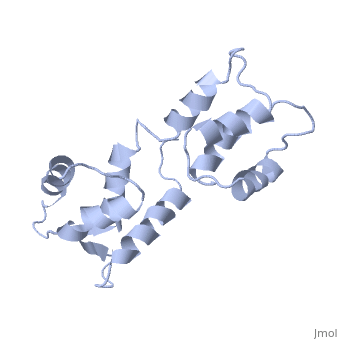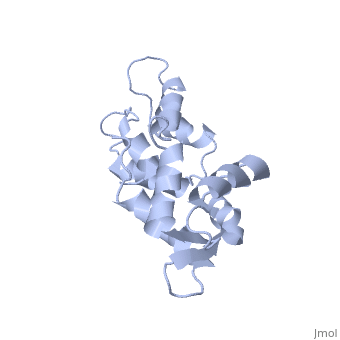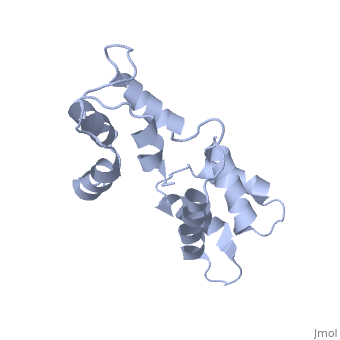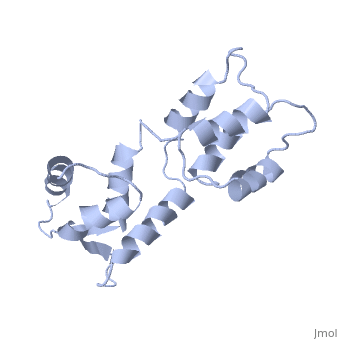
[[1cfc]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [ | <StructureSection load='1cfc' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1cfc]]' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | |||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1cfc]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Xenopus_laevis Xenopus laevis]. Full experimental information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1CFC OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1CFC FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">Solution NMR</td></tr> | |||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1cfc FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1cfc OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1cfc PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1cfc RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1cfc PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1cfc ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
== Function == | |||
[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CALM1_XENLA CALM1_XENLA] Calmodulin mediates the control of a large number of enzymes, ion channels and other proteins by Ca(2+). Among the enzymes to be stimulated by the calmodulin-Ca(2+) complex are a number of protein kinases and phosphatases. | |||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | |||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | |||
Check<jmol> | |||
<jmolCheckbox> | |||
<scriptWhenChecked>; select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/cf/1cfc_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | |||
<scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | |||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | |||
</jmolCheckbox> | |||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=1cfc ConSurf]. | |||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
The three-dimensional structure of calmodulin in the absence of Ca2+ has been determined by three- and four-dimensional heteronuclear NMR experiments, including ROE, isotope-filtering combined with reverse labelling, and measurement of more than 700 three-bond J-couplings. In analogy with the Ca(2+)-ligated state of this protein, it consists of two small globular domains separated by a flexible linker, with no stable, direct contacts between the two domains. In the absence of Ca2+, the four helices in each of the two globular domains form a highly twisted bundle, capped by a short anti-parallel beta-sheet. This arrangement is qualitatively similar to that observed in the crystal structure of the Ca(2+)-free N-terminal domain of troponin C. | |||
Solution structure of calcium-free calmodulin.,Kuboniwa H, Tjandra N, Grzesiek S, Ren H, Klee CB, Bax A Nat Struct Biol. 1995 Sep;2(9):768-76. PMID:7552748<ref>PMID:7552748</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
<div class="pdbe-citations 1cfc" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Calmodulin|Calmodulin]] | *[[Calmodulin 3D structures|Calmodulin 3D structures]] | ||
*[[Hydrogen in macromolecular models|Hydrogen in macromolecular models]] | *[[Hydrogen in macromolecular models|Hydrogen in macromolecular models]] | ||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
__TOC__ | |||
== | </StructureSection> | ||
< | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
[[Category: Xenopus laevis]] | [[Category: Xenopus laevis]] | ||
[[Category: Bax | [[Category: Bax A]] | ||
[[Category: Grzesiek | [[Category: Grzesiek S]] | ||
[[Category: Klee | [[Category: Klee CB]] | ||
[[Category: Kuboniwa | [[Category: Kuboniwa H]] | ||
[[Category: Ren | [[Category: Ren H]] | ||
[[Category: Tjandra | [[Category: Tjandra N]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:21, 22 May 2024
CALCIUM-FREE CALMODULINCALCIUM-FREE CALMODULIN
Structural highlights
FunctionCALM1_XENLA Calmodulin mediates the control of a large number of enzymes, ion channels and other proteins by Ca(2+). Among the enzymes to be stimulated by the calmodulin-Ca(2+) complex are a number of protein kinases and phosphatases. Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedThe three-dimensional structure of calmodulin in the absence of Ca2+ has been determined by three- and four-dimensional heteronuclear NMR experiments, including ROE, isotope-filtering combined with reverse labelling, and measurement of more than 700 three-bond J-couplings. In analogy with the Ca(2+)-ligated state of this protein, it consists of two small globular domains separated by a flexible linker, with no stable, direct contacts between the two domains. In the absence of Ca2+, the four helices in each of the two globular domains form a highly twisted bundle, capped by a short anti-parallel beta-sheet. This arrangement is qualitatively similar to that observed in the crystal structure of the Ca(2+)-free N-terminal domain of troponin C. Solution structure of calcium-free calmodulin.,Kuboniwa H, Tjandra N, Grzesiek S, Ren H, Klee CB, Bax A Nat Struct Biol. 1995 Sep;2(9):768-76. PMID:7552748[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences |
| ||||||||||||||||