2vgb: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==HUMAN ERYTHROCYTE PYRUVATE KINASE== | |||
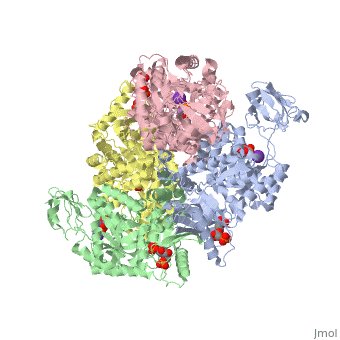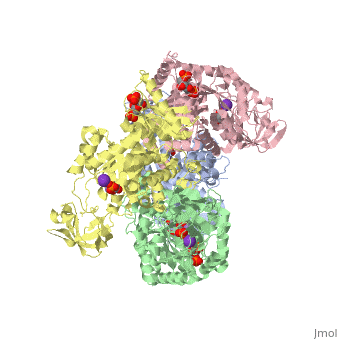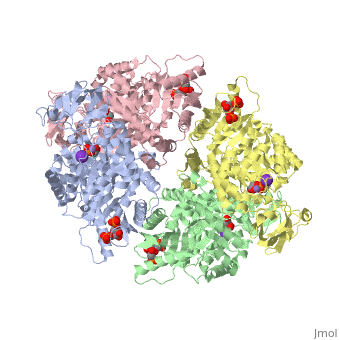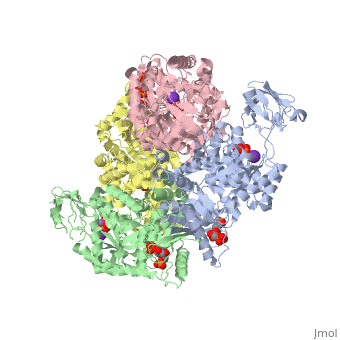
<StructureSection load='2vgb' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2vgb]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.73Å' scene=''> | |||
== Structural highlights == | |||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2vgb]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. This structure supersedes the now removed PDB entry [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/send-pdb?obs=1&id=1liu 1liu]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2VGB OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2VGB FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.73Å</td></tr> | |||
<tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=FBP:BETA-FRUCTOSE-1,6-DIPHOSPHATE'>FBP</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=K:POTASSIUM+ION'>K</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=MN:MANGANESE+(II)+ION'>MN</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=PGA:2-PHOSPHOGLYCOLIC+ACID'>PGA</scene></td></tr> | |||
== | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2vgb FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2vgb OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2vgb PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2vgb RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2vgb PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2vgb ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | ||
[[2vgb]] is a 4 chain structure with sequence from [ | </table> | ||
== Disease == | |||
[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/KPYR_HUMAN KPYR_HUMAN] Defects in PKLR are the cause of pyruvate kinase hyperactivity (PKHYP) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/102900 102900]; also known as high red cell ATP syndrome. This autosomal dominant phenotype is characterized by increase of red blood cell ATP.<ref>PMID:9090535</ref> Defects in PKLR are the cause of pyruvate kinase deficiency of red cells (PKRD) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/266200 266200]. A frequent cause of hereditary non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia. Clinically, pyruvate kinase-deficient patients suffer from a highly variable degree of chronic hemolysis, ranging from severe neonatal jaundice and fatal anemia at birth, severe transfusion-dependent chronic hemolysis, moderate hemolysis with exacerbation during infection, to a fully compensated hemolysis without apparent anemia. | |||
== Function == | |||
[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/KPYR_HUMAN KPYR_HUMAN] Plays a key role in glycolysis (By similarity). | |||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | |||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | |||
Check<jmol> | |||
<jmolCheckbox> | |||
<scriptWhenChecked>; select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/vg/2vgb_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | |||
<scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | |||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | |||
</jmolCheckbox> | |||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=2vgb ConSurf]. | |||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Pyruvate Kinase|Pyruvate Kinase]] | *[[Pyruvate Kinase|Pyruvate Kinase]] | ||
*[[Pyruvate kinase 3D structures|Pyruvate kinase 3D structures]] | |||
== | == References == | ||
< | <references/> | ||
__TOC__ | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
[[Category: Homo sapiens]] | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
[[Category: Abraham | [[Category: Abraham DJ]] | ||
[[Category: Bianchi | [[Category: Bianchi P]] | ||
[[Category: Chiarelli | [[Category: Chiarelli L]] | ||
[[Category: Dolzan | [[Category: Dolzan M]] | ||
[[Category: Fortin | [[Category: Fortin R]] | ||
[[Category: Galizzi | [[Category: Galizzi A]] | ||
[[Category: Mattevi | [[Category: Mattevi A]] | ||
[[Category: Valentini | [[Category: Valentini G]] | ||
[[Category: Wang | [[Category: Wang C]] | ||
[[Category: Zanella | [[Category: Zanella A]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:07, 1 May 2024
HUMAN ERYTHROCYTE PYRUVATE KINASEHUMAN ERYTHROCYTE PYRUVATE KINASE
Structural highlights
DiseaseKPYR_HUMAN Defects in PKLR are the cause of pyruvate kinase hyperactivity (PKHYP) [MIM:102900; also known as high red cell ATP syndrome. This autosomal dominant phenotype is characterized by increase of red blood cell ATP.[1] Defects in PKLR are the cause of pyruvate kinase deficiency of red cells (PKRD) [MIM:266200. A frequent cause of hereditary non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia. Clinically, pyruvate kinase-deficient patients suffer from a highly variable degree of chronic hemolysis, ranging from severe neonatal jaundice and fatal anemia at birth, severe transfusion-dependent chronic hemolysis, moderate hemolysis with exacerbation during infection, to a fully compensated hemolysis without apparent anemia. FunctionKPYR_HUMAN Plays a key role in glycolysis (By similarity). Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||