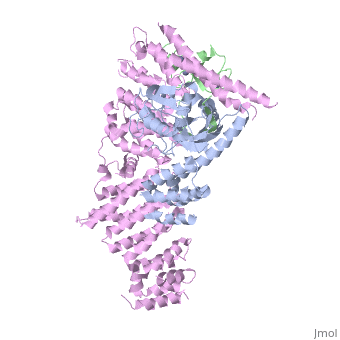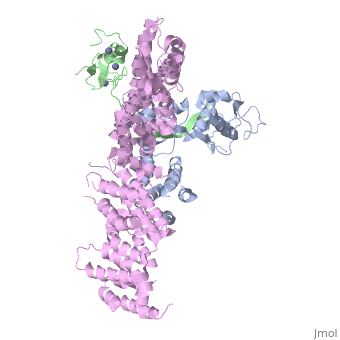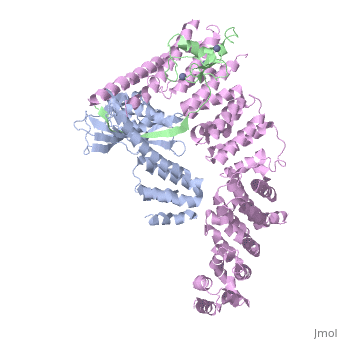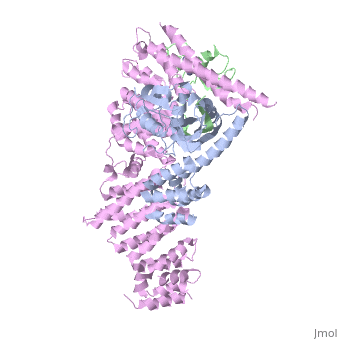4f52: Difference between revisions
New page: '''Unreleased structure''' The entry 4f52 is ON HOLD Authors: Duda, D.M., Olszewski, J.L., Schulman, B.A. Description: Structure of a Glomulin-RBX1-CUL1 complex |
No edit summary |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The | ==Structure of a Glomulin-RBX1-CUL1 complex== | ||
<StructureSection load='4f52' size='340' side='right'caption='[[4f52]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.00Å' scene=''> | |||
== Structural highlights == | |||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[4f52]] is a 6 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=4F52 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4F52 FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 3Å</td></tr> | |||
<tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=ZN:ZINC+ION'>ZN</scene></td></tr> | |||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4f52 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=4f52 OCA], [https://pdbe.org/4f52 PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=4f52 RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/4f52 PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=4f52 ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
== Function == | |||
[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CUL1_HUMAN CUL1_HUMAN] Core component of multiple cullin-RING-based SCF (SKP1-CUL1-F-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complexes, which mediate the ubiquitination of proteins involved in cell cycle progression, signal transduction and transcription. In the SCF complex, serves as a rigid scaffold that organizes the SKP1-F-box protein and RBX1 subunits. May contribute to catalysis through positioning of the substrate and the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. The E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity of the complex is dependent on the neddylation of the cullin subunit and is inhibited by the association of the deneddylated cullin subunit with TIP120A/CAND1. The functional specificity of the SCF complex depends on the F-box protein as substrate recognition component. SCF(BTRC) and SCF(FBXW11) direct ubiquitination of CTNNB1 and participate in Wnt signaling. SCF(FBXW11) directs ubiquitination of phosphorylated NFKBIA. SCF(BTRC) directs ubiquitination of NFKBIB, NFKBIE, ATF4, SMAD3, SMAD4, CDC25A, FBXO5 and probably NFKB2. SCF(SKP2) directs ubiquitination of phosphorylated CDKN1B/p27kip and is involved in regulation of G1/S transition. SCF(SKP2) directs ubiquitination of ORC1, CDT1, RBL2, ELF4, CDKN1A, RAG2, FOXO1A, and probably MYC and TAL1. SCF(FBXW7) directs ubiquitination of cyclin E, NOTCH1 released notch intracellular domain (NICD), and probably PSEN1. SCF(FBXW2) directs ubiquitination of GCM1. SCF(FBXO32) directs ubiquitination of MYOD1. SCF(FBXO7) directs ubiquitination of BIRC2 and DLGAP5. SCF(FBXO33) directs ubiquitination of YBX1. SCF(FBXO11) does not seem to direct ubiquitination of TP53. SCF(BTRC) mediates the ubiquitination of NFKBIA at 'Lys-21' and 'Lys-22'; the degradation frees the associated NFKB1-RELA dimer to translocate into the nucleus and to activate transcription. SCF(Cyclin F) directs ubiquitination of CP110 (By similarity).<ref>PMID:9663463</ref> <ref>PMID:15531760</ref> <ref>PMID:15640526</ref> <ref>PMID:18644861</ref> <ref>PMID:19679664</ref> | |||
==See Also== | |||
*[[Cullin 3D structures|Cullin 3D structures]] | |||
*[[RING box protein|RING box protein]] | |||
*[[Ring box protein 3D structures|Ring box protein 3D structures]] | |||
*[[Ubiquitin protein ligase 3D structures|Ubiquitin protein ligase 3D structures]] | |||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
__TOC__ | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
[[Category: Homo sapiens]] | |||
[[Category: Large Structures]] | |||
[[Category: Duda DM]] | |||
[[Category: Olszewski JL]] | |||
[[Category: Schulman BA]] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:10, 1 March 2024
Structure of a Glomulin-RBX1-CUL1 complexStructure of a Glomulin-RBX1-CUL1 complex
Structural highlights
FunctionCUL1_HUMAN Core component of multiple cullin-RING-based SCF (SKP1-CUL1-F-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complexes, which mediate the ubiquitination of proteins involved in cell cycle progression, signal transduction and transcription. In the SCF complex, serves as a rigid scaffold that organizes the SKP1-F-box protein and RBX1 subunits. May contribute to catalysis through positioning of the substrate and the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. The E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity of the complex is dependent on the neddylation of the cullin subunit and is inhibited by the association of the deneddylated cullin subunit with TIP120A/CAND1. The functional specificity of the SCF complex depends on the F-box protein as substrate recognition component. SCF(BTRC) and SCF(FBXW11) direct ubiquitination of CTNNB1 and participate in Wnt signaling. SCF(FBXW11) directs ubiquitination of phosphorylated NFKBIA. SCF(BTRC) directs ubiquitination of NFKBIB, NFKBIE, ATF4, SMAD3, SMAD4, CDC25A, FBXO5 and probably NFKB2. SCF(SKP2) directs ubiquitination of phosphorylated CDKN1B/p27kip and is involved in regulation of G1/S transition. SCF(SKP2) directs ubiquitination of ORC1, CDT1, RBL2, ELF4, CDKN1A, RAG2, FOXO1A, and probably MYC and TAL1. SCF(FBXW7) directs ubiquitination of cyclin E, NOTCH1 released notch intracellular domain (NICD), and probably PSEN1. SCF(FBXW2) directs ubiquitination of GCM1. SCF(FBXO32) directs ubiquitination of MYOD1. SCF(FBXO7) directs ubiquitination of BIRC2 and DLGAP5. SCF(FBXO33) directs ubiquitination of YBX1. SCF(FBXO11) does not seem to direct ubiquitination of TP53. SCF(BTRC) mediates the ubiquitination of NFKBIA at 'Lys-21' and 'Lys-22'; the degradation frees the associated NFKB1-RELA dimer to translocate into the nucleus and to activate transcription. SCF(Cyclin F) directs ubiquitination of CP110 (By similarity).[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] See Also
References
|
| ||||||||||||||||||