1j7n: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Anthrax Toxin Lethal factor== | |||
<StructureSection load='1j7n' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1j7n]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.30Å' scene=''> | |||
== Structural highlights == | |||
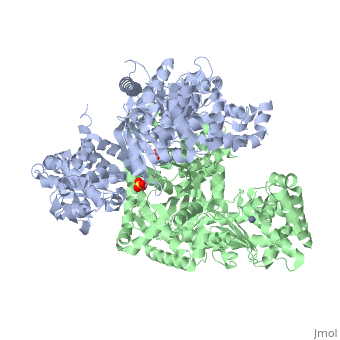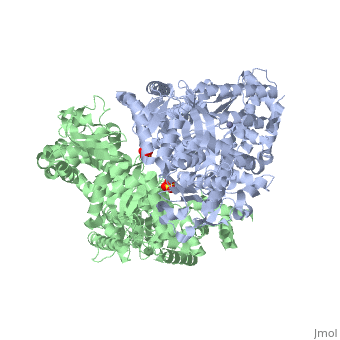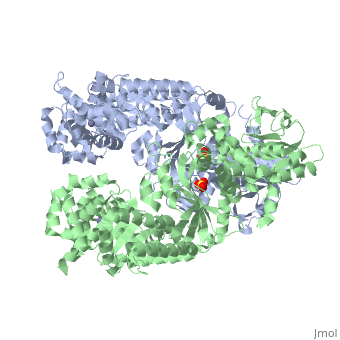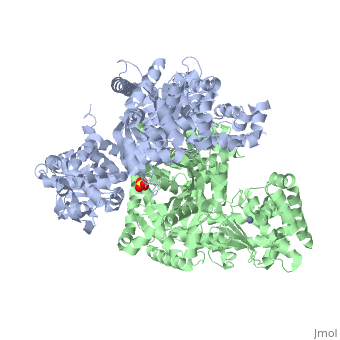
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1j7n]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bacillus_anthracis Bacillus anthracis]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1J7N OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1J7N FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.3Å</td></tr> | |||
<tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=SO4:SULFATE+ION'>SO4</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=ZN:ZINC+ION'>ZN</scene></td></tr> | |||
== | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1j7n FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1j7n OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1j7n PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1j7n RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1j7n PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1j7n ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | ||
[[1j7n]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [ | </table> | ||
== Function == | |||
[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/LEF_BACAN LEF_BACAN] One of the three proteins composing the anthrax toxin, the agent which infects many mammalian species and that may cause death. LF is the lethal factor that, when associated with PA, causes death. LF is not toxic by itself. It is a protease that cleaves the N-terminal of most dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases (MAPKKs or MAP2Ks) (except for MAP2K5). Cleavage invariably occurs within the N-terminal proline-rich region preceding the kinase domain, thus disrupting a sequence involved in directing specific protein-protein interactions necessary for the assembly of signaling complexes. There may be other cytosolic targets of LF involved in cytotoxicity. The proteasome may mediate a toxic process initiated by LF in the cell cytosol involving degradation of unidentified molecules that are essential for macrophage homeostasis. This is an early step in LeTx intoxication, but it is downstream of the cleavage by LF of MEK1 or other putative substrates.<ref>PMID:9563949</ref> <ref>PMID:9703991</ref> <ref>PMID:10475971</ref> <ref>PMID:11104681</ref> <ref>PMID:10338520</ref> | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Anthrax Lethal Factor|Anthrax Lethal Factor]] | *[[Anthrax Lethal Factor|Anthrax Lethal Factor]] | ||
*[[Anthrax lethal factor 3D structures|Anthrax lethal factor 3D structures]] | |||
== | == References == | ||
< | <references/> | ||
__TOC__ | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
[[Category: Bacillus anthracis]] | [[Category: Bacillus anthracis]] | ||
[[Category: Bienkowska | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
[[Category: Collier | [[Category: Bienkowska J]] | ||
[[Category: Hanna | [[Category: Collier RJ]] | ||
[[Category: Lacy | [[Category: Hanna P]] | ||
[[Category: Leppla | [[Category: Lacy DB]] | ||
[[Category: Liddington | [[Category: Leppla SH]] | ||
[[Category: Pannifer | [[Category: Liddington RC]] | ||
[[Category: Park | [[Category: Pannifer AD]] | ||
[[Category: Petosa | [[Category: Park S]] | ||
[[Category: Renatus | [[Category: Petosa C]] | ||
[[Category: Schwarzenbacher | [[Category: Renatus M]] | ||
[[Category: Wong | [[Category: Schwarzenbacher R]] | ||
[[Category: Wong TY]] | |||
Latest revision as of 10:37, 7 February 2024
Anthrax Toxin Lethal factorAnthrax Toxin Lethal factor
Structural highlights
FunctionLEF_BACAN One of the three proteins composing the anthrax toxin, the agent which infects many mammalian species and that may cause death. LF is the lethal factor that, when associated with PA, causes death. LF is not toxic by itself. It is a protease that cleaves the N-terminal of most dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases (MAPKKs or MAP2Ks) (except for MAP2K5). Cleavage invariably occurs within the N-terminal proline-rich region preceding the kinase domain, thus disrupting a sequence involved in directing specific protein-protein interactions necessary for the assembly of signaling complexes. There may be other cytosolic targets of LF involved in cytotoxicity. The proteasome may mediate a toxic process initiated by LF in the cell cytosol involving degradation of unidentified molecules that are essential for macrophage homeostasis. This is an early step in LeTx intoxication, but it is downstream of the cleavage by LF of MEK1 or other putative substrates.[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||