1aoi: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
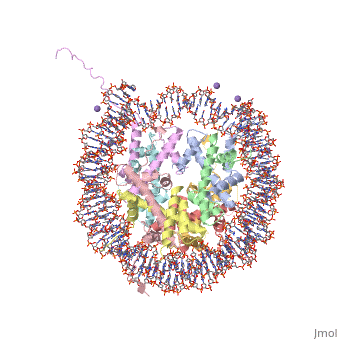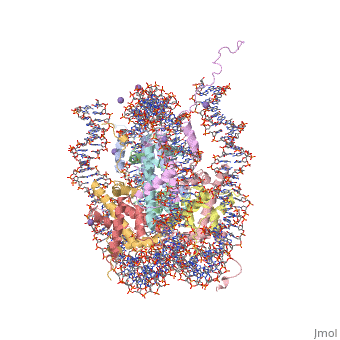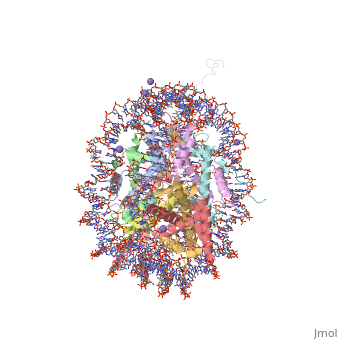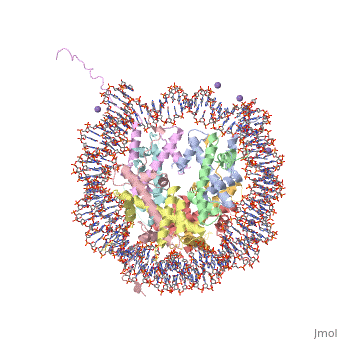
==COMPLEX BETWEEN NUCLEOSOME CORE PARTICLE (H3,H4,H2A,H2B) AND 146 BP LONG DNA FRAGMENT== | ==COMPLEX BETWEEN NUCLEOSOME CORE PARTICLE (H3,H4,H2A,H2B) AND 146 BP LONG DNA FRAGMENT== | ||
<StructureSection load='1aoi' size='340' side='right' caption='[[1aoi]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.80Å' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1aoi' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1aoi]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.80Å' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1aoi]] is a 10 chain structure with sequence from [ | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1aoi]] is a 10 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Xenopus_laevis Xenopus laevis]. The July 2000 RCSB PDB [https://pdb.rcsb.org/pdb/static.do?p=education_discussion/molecule_of_the_month/index.html Molecule of the Month] feature on ''Nucleosome'' by David S. Goodsell is [https://dx.doi.org/10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2000_7 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2000_7]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1AOI OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1AOI FirstGlance]. <br> | ||
</td></tr><tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=MN:MANGANESE+(II)+ION'>MN</scene>< | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.8Å</td></tr> | ||
<tr><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[ | <tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=MN:MANGANESE+(II)+ION'>MN</scene></td></tr> | ||
<table> | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1aoi FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1aoi OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1aoi PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1aoi RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1aoi PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1aoi ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | ||
</table> | |||
== Function == | |||
[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/H2B11_XENLA H2B11_XENLA] Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling. | |||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | ||
Check<jmol> | Check<jmol> | ||
<jmolCheckbox> | <jmolCheckbox> | ||
<scriptWhenChecked>select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/ao/1aoi_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | <scriptWhenChecked>; select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/ao/1aoi_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | ||
<scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | <scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | ||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | <text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | ||
</jmolCheckbox> | </jmolCheckbox> | ||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/ | </jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=1aoi ConSurf]. | ||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | <div style="clear:both"></div> | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Histone|Histone]] | *[[Histone 3D structures|Histone 3D structures]] | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
[[Category: Large Structures]] | |||
[[Category: Nucleosome]] | [[Category: Nucleosome]] | ||
[[Category: RCSB PDB Molecule of the Month]] | [[Category: RCSB PDB Molecule of the Month]] | ||
[[Category: Xenopus laevis]] | [[Category: Xenopus laevis]] | ||
[[Category: Luger | [[Category: Luger K]] | ||
[[Category: Maeder | [[Category: Maeder AW]] | ||
[[Category: Richmond | [[Category: Richmond RK]] | ||
[[Category: Richmond | [[Category: Richmond TJ]] | ||
[[Category: Sargent | [[Category: Sargent DF]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:32, 7 February 2024
COMPLEX BETWEEN NUCLEOSOME CORE PARTICLE (H3,H4,H2A,H2B) AND 146 BP LONG DNA FRAGMENTCOMPLEX BETWEEN NUCLEOSOME CORE PARTICLE (H3,H4,H2A,H2B) AND 146 BP LONG DNA FRAGMENT
Structural highlights
FunctionH2B11_XENLA Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling. Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. See Also |
| ||||||||||||||||||