2vzi: Difference between revisions
New page: '''Unreleased structure''' The entry 2vzi is ON HOLD Authors: Lorenz, S., Vakonakis, I., Lowe, E.D., Campbell, I.D., Noble, M.E.M., Hoellerer, M.K. Description: Crystal structure of th... |
No edit summary |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
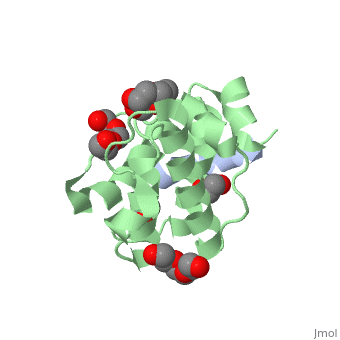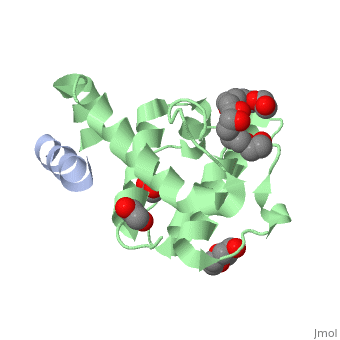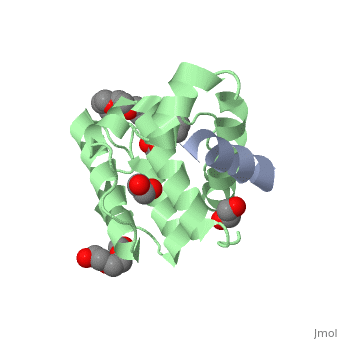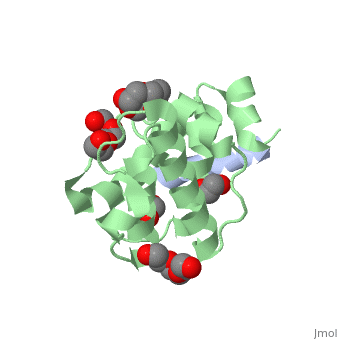
The | ==Crystal structure of the C-terminal calponin homology domain of alpha- parvin in complex with paxillin LD4 motif== | ||
<StructureSection load='2vzi' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2vzi]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.20Å' scene=''> | |||
== Structural highlights == | |||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2vzi]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2VZI OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2VZI FirstGlance]. <br> | |||
</td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.2Å</td></tr> | |||
<tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=EDO:1,2-ETHANEDIOL'>EDO</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=PG4:TETRAETHYLENE+GLYCOL'>PG4</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=PGE:TRIETHYLENE+GLYCOL'>PGE</scene></td></tr> | |||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2vzi FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2vzi OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2vzi PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2vzi RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2vzi PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2vzi ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
== Function == | |||
[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/PAXI_HUMAN PAXI_HUMAN] Cytoskeletal protein involved in actin-membrane attachment at sites of cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix (focal adhesion). | |||
== Evolutionary Conservation == | |||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | |||
Check<jmol> | |||
<jmolCheckbox> | |||
<scriptWhenChecked>; select protein; define ~consurf_to_do selected; consurf_initial_scene = true; script "/wiki/ConSurf/vz/2vzi_consurf.spt"</scriptWhenChecked> | |||
<scriptWhenUnchecked>script /wiki/extensions/Proteopedia/spt/initialview01.spt</scriptWhenUnchecked> | |||
<text>to colour the structure by Evolutionary Conservation</text> | |||
</jmolCheckbox> | |||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=2vzi ConSurf]. | |||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | |||
<div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | |||
== Publication Abstract from PubMed == | |||
The adaptor protein paxillin contains five conserved leucine-rich (LD) motifs that interact with a variety of focal adhesion proteins, such as alpha-parvin. Here, we report the first crystal structure of the C-terminal calponin homology domain (CH(C)) of alpha-parvin at 1.05 A resolution and show that it is able to bind all the LD motifs, with some selectivity for LD1, LD2, and LD4. Cocrystal structures with these LD motifs reveal the molecular details of their interactions with a common binding site on alpha-parvin-CH(C), which is located at the rim of the canonical fold and includes part of the inter-CH domain linker. Surprisingly, this binding site can accommodate LD motifs in two antiparallel orientations. Taken together, these results reveal an unusual degree of binding degeneracy in the paxillin/alpha-parvin system that may facilitate the assembly of dynamic signaling complexes in the cell. | |||
Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin.,Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607<ref>PMID:18940607</ref> | |||
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | |||
</div> | |||
<div class="pdbe-citations 2vzi" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | |||
==See Also== | |||
*[[Parvin|Parvin]] | |||
*[[Parvin 3D structures|Parvin 3D structures]] | |||
*[[Paxillin|Paxillin]] | |||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
__TOC__ | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
[[Category: Homo sapiens]] | |||
[[Category: Large Structures]] | |||
[[Category: Campbell ID]] | |||
[[Category: Hoellerer MK]] | |||
[[Category: Lorenz S]] | |||
[[Category: Lowe ED]] | |||
[[Category: Noble MEM]] | |||
[[Category: Vakonakis I]] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:38, 13 December 2023
Crystal structure of the C-terminal calponin homology domain of alpha- parvin in complex with paxillin LD4 motifCrystal structure of the C-terminal calponin homology domain of alpha- parvin in complex with paxillin LD4 motif
Structural highlights
FunctionPAXI_HUMAN Cytoskeletal protein involved in actin-membrane attachment at sites of cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix (focal adhesion). Evolutionary Conservation Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Publication Abstract from PubMedThe adaptor protein paxillin contains five conserved leucine-rich (LD) motifs that interact with a variety of focal adhesion proteins, such as alpha-parvin. Here, we report the first crystal structure of the C-terminal calponin homology domain (CH(C)) of alpha-parvin at 1.05 A resolution and show that it is able to bind all the LD motifs, with some selectivity for LD1, LD2, and LD4. Cocrystal structures with these LD motifs reveal the molecular details of their interactions with a common binding site on alpha-parvin-CH(C), which is located at the rim of the canonical fold and includes part of the inter-CH domain linker. Surprisingly, this binding site can accommodate LD motifs in two antiparallel orientations. Taken together, these results reveal an unusual degree of binding degeneracy in the paxillin/alpha-parvin system that may facilitate the assembly of dynamic signaling complexes in the cell. Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin.,Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607[1] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||