Stathmin: Difference between revisions
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
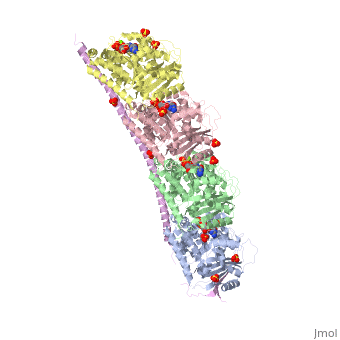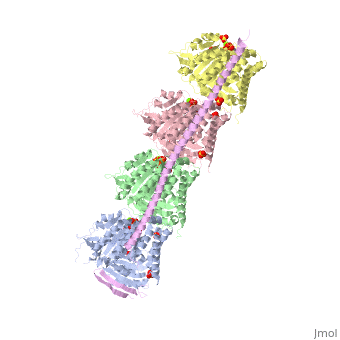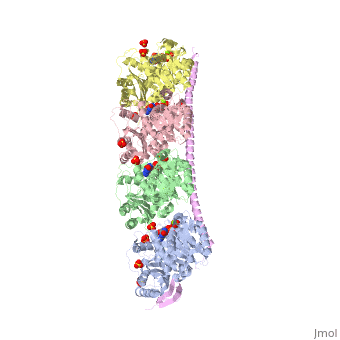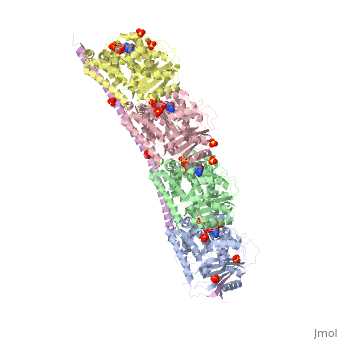
<StructureSection load='3ryf' size='340' side='right' caption='Rat stathmin SLD domain (magenta) complex with tubulin α chain (grey, pink), tubulin β chain (green, yellow), GTP, sulfate and Mg+2 ions (PDB code [[3ryf]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='3ryf' size='340' side='right' caption='Rat stathmin SLD domain (magenta) complex with tubulin α chain (grey, pink), tubulin β chain (green, yellow), GTP, sulfate and Mg+2 ions (PDB code [[3ryf]])' scene=''> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Stathmin''' (STM) regulates microtubules dynamics. Microtubules undergo continuous assembly and disassembly in the cell’s cytoskeleton. STM binds to tubulin and prevents the latter from polymerization thus preventing microtubule assembly. Phosphorylation of STM weakens the binding of STM to tubulin enabling the microtubule assembly needed for the formation of mitotic spindle. Thus, STM is an oncoprotein. STM contains an SLD (Stathmin-Like Domain) domain of 149 residues which binds the tubulin dimer<ref>PMID:15216892</ref>. | '''Stathmin-4''' (STM-4) or '''stathmin-like protein B3''' regulates microtubules dynamics. Microtubules undergo continuous assembly and disassembly in the cell’s cytoskeleton. STM-4 binds to tubulin and prevents the latter from polymerization thus preventing microtubule assembly. Phosphorylation of STM-4 weakens the binding of STM-4 to tubulin enabling the microtubule assembly needed for the formation of mitotic spindle. Thus, STM-4 is an oncoprotein. STM-4 contains an SLD (Stathmin-Like Domain) domain of 149 residues which binds the tubulin dimer<ref>PMID:15216892</ref>. | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Decreased levels of STM are found in brains of adults with Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease<ref>PMID:11771751</ref>. | Decreased levels of STM-4 are found in brains of adults with Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease<ref>PMID:11771751</ref>. | ||
== 3D Structures of stathmin-4 == | |||
[[Stathmin-4 3D structures]] | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:02, 4 December 2023
FunctionStathmin-4 (STM-4) or stathmin-like protein B3 regulates microtubules dynamics. Microtubules undergo continuous assembly and disassembly in the cell’s cytoskeleton. STM-4 binds to tubulin and prevents the latter from polymerization thus preventing microtubule assembly. Phosphorylation of STM-4 weakens the binding of STM-4 to tubulin enabling the microtubule assembly needed for the formation of mitotic spindle. Thus, STM-4 is an oncoprotein. STM-4 contains an SLD (Stathmin-Like Domain) domain of 149 residues which binds the tubulin dimer[1]. DiseaseDecreased levels of STM-4 are found in brains of adults with Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease[2]. 3D Structures of stathmin-4
|
| ||||||||||
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Curmi PA, Gavet O, Charbaut E, Ozon S, Lachkar-Colmerauer S, Manceau V, Siavoshian S, Maucuer A, Sobel A. Stathmin and its phosphoprotein family: general properties, biochemical and functional interaction with tubulin. Cell Struct Funct. 1999 Oct;24(5):345-57. PMID:15216892
- ↑ Cheon MS, Fountoulakis M, Cairns NJ, Dierssen M, Herkner K, Lubec G. Decreased protein levels of stathmin in adult brains with Down syndrome and Alzheimer's disease. J Neural Transm Suppl. 2001;(61):281-8. PMID:11771751