4n3z: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[4n3z]] is a 3 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=4N3Z OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4N3Z FirstGlance]. <br> | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[4n3z]] is a 3 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=4N3Z OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4N3Z FirstGlance]. <br> | ||
</td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=PO4:PHOSPHATE+ION'>PO4</scene></td></tr> | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 3.1Å</td></tr> | ||
<tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=PO4:PHOSPHATE+ION'>PO4</scene></td></tr> | |||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4n3z FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=4n3z OCA], [https://pdbe.org/4n3z PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=4n3z RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/4n3z PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=4n3z ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4n3z FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=4n3z OCA], [https://pdbe.org/4n3z PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=4n3z RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/4n3z PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=4n3z ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:45, 8 November 2023
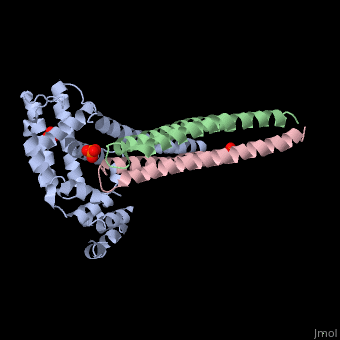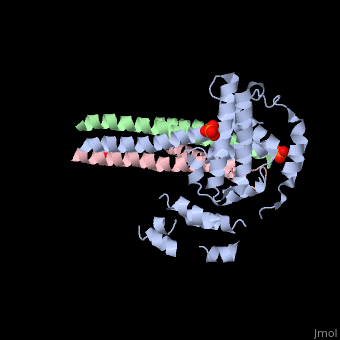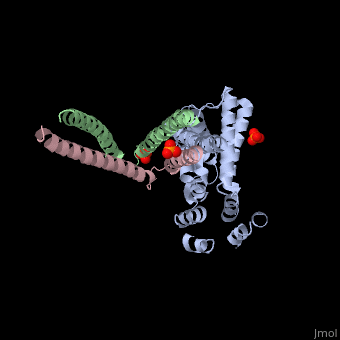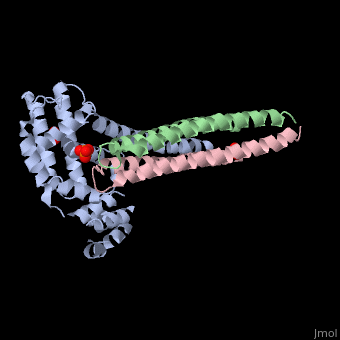
Crystal structure of Rabex-5delta and Rabaptin-5C21 complexCrystal structure of Rabex-5delta and Rabaptin-5C21 complex
Structural highlights
FunctionRABX5_HUMAN Rab effector protein acting as linker between gamma-adaptin, RAB4A or RAB5A. Involved in endocytic membrane fusion and membrane trafficking of recycling endosomes. Stimulates nucleotide exchange on RAB5A. Can act as a ubiquitin ligase (By similarity).[1] [2] [3] Publication Abstract from PubMedRabex-5 and Rabaptin-5 function together to activate Rab5 and further promote early endosomal fusion in endocytosis. The Rabex-5 GEF activity is autoinhibited by the Rabex-5 CC domain (Rabex-5CC) and activated by the Rabaptin-5 C2-1 domain (Rabaptin-5C21) with yet unknown mechanism. We report here the crystal structures of Rabex-5 in complex with the dimeric Rabaptin-5C21 (Rabaptin-5C212) and in complex with Rabaptin-5C212 and Rab5, along with biophysical and biochemical analyses. We show that Rabex-5CC assumes an amphipathic alpha-helix which binds weakly to the substrate-binding site of the GEF domain, leading to weak autoinhibition of the GEF activity. Binding of Rabaptin-5C21 to Rabex-5 displaces Rabex-5CC to yield a largely exposed substrate-binding site, leading to release of the GEF activity. In the ternary complex the substrate-binding site of Rabex-5 is completely exposed to bind and activate Rab5. Our results reveal the molecular mechanism for the regulation of the Rabex-5 GEF activity. Molecular mechanism for Rabex-5 GEF activation by Rabaptin-5.,Zhang Z, Zhang T, Wang S, Gong Z, Tang C, Chen J, Ding J Elife (Cambridge). 2014 Jun 23:e02687. doi: 10.7554/eLife.02687. PMID:24957337[4] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||