Glycogenolysis: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
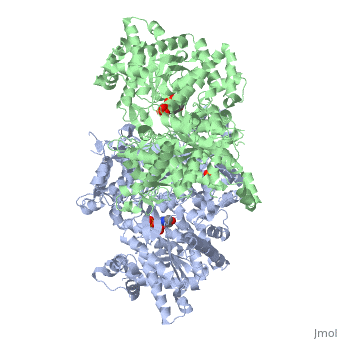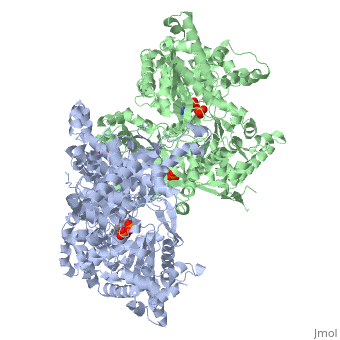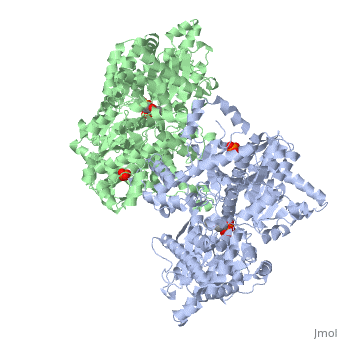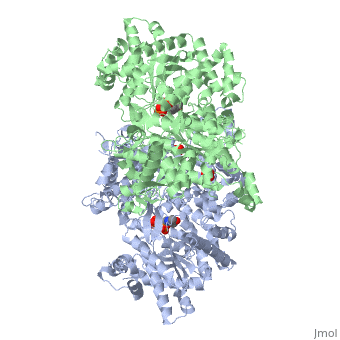
New page: <StructureSection load='1ygp' size='350' side='right' caption='Yeast glycogen phosphorylase dimer with pyridoxal-5-phosphate and phosphate (PDB entry 1ygp)' scene=''> This is a default... |
No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<StructureSection load='1ygp' size='350' side='right' caption='Yeast glycogen phosphorylase dimer with pyridoxal-5-phosphate and phosphate (PDB entry [[1ygp]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1ygp' size='350' side='right' caption='Yeast glycogen phosphorylase dimer with pyridoxal-5-phosphate and phosphate (PDB entry [[1ygp]])' scene=''> | ||
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen (n) to <scene name='94/942621/Cv/3'>glucose-1-phosphate</scene> and glycogen (n-1). Glycogen branches are catabolized by the sequential removal of glucose monomers via phosphorolysis, by the enzyme [[Glycogen Phosphorylase|glycogen phosphorylase]]. | |||
glycogen(n residues) + Pi ⇌ glycogen(n-1 residues) + glucose-1-phosphate | |||
Here, glycogen phosphorylase cleaves the bond linking a terminal glucose residue to a glycogen branch by substitution of a phosphoryl group for the α[1→4] linkage. Glucose-1-phosphate is converted to <scene name='94/942621/Cv/2'>glucose-1,6-bisphosphate</scene> (which often ends up in [[glycolysis]]) by the enzyme phosphoglucomutase. | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Latest revision as of 18:42, 18 December 2022
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen (n) to and glycogen (n-1). Glycogen branches are catabolized by the sequential removal of glucose monomers via phosphorolysis, by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase. glycogen(n residues) + Pi ⇌ glycogen(n-1 residues) + glucose-1-phosphate Here, glycogen phosphorylase cleaves the bond linking a terminal glucose residue to a glycogen branch by substitution of a phosphoryl group for the α[1→4] linkage. Glucose-1-phosphate is converted to (which often ends up in glycolysis) by the enzyme phosphoglucomutase. |
| ||||||||||