Apoptotic protease-activating factor: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
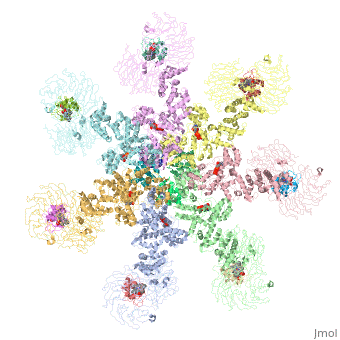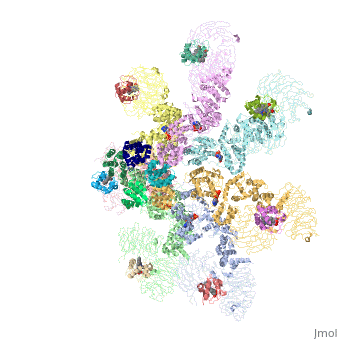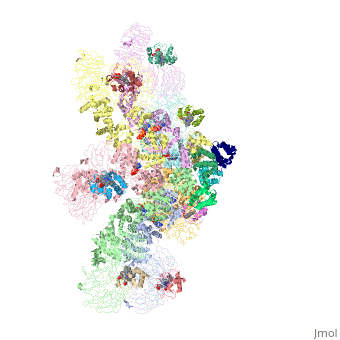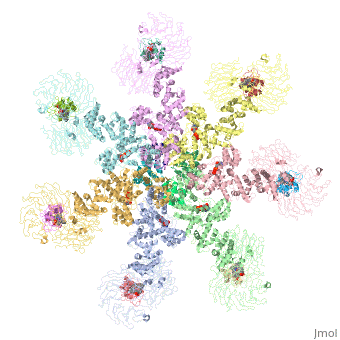
<StructureSection load='5juy' size='340' side='right' caption='Human apoptosis protease-activating factor-1 | <StructureSection load='5juy' size='340' side='right' caption='Human apoptosis protease-activating factor-1 complex with cytochrome c and caspase 9 forming the apoptosome (PDB entry [[5juy]]) ' scene='77/774059/Cv/2'> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Apoptosis protease-activating factor-1''' (APAF-1) binds to cytochrome c and ATP to form the apoptosome which leads to the recruitment and activation of caspase 9 by cleaving the procaspase 9. Caspase 9 is involved in executing the apoptosis of cells<ref>PMID:15829969</ref>. | '''Apoptosis protease-activating factor-1''' or '''Apoptosis peptidase-activating factor-1''' (APAF-1) binds to cytochrome c and ATP to form the apoptosome which leads to the recruitment and activation of caspase 9 by cleaving the procaspase 9. Caspase 9 is involved in executing the apoptosis of cells<ref>PMID:15829969</ref>. | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
Apaf-1 contains several copies of the WD-40 domain which are involved in binding to cytochrome c<ref>PMID:26014357</ref>., caspase recruitment domain (CARD) and an ATPase domain. | Apaf-1 contains several copies of the WD-40 domain which are involved in binding to cytochrome c<ref>PMID:26014357</ref>., caspase recruitment domain (CARD) and an ATPase domain. | ||
</ | *<scene name='77/774059/Cv/3'>Apoptosome</scene> formed by Human apoptosis protease-activating factor-1 (green; subunits A, B, C, D, E, F, G) complex with cytochrome c (red; subunits H, I, J, K, L, M, N) and caspase 9 (magenta; subunits O, P, Q, R) (PDB entry [[5juy]]). | ||
==3D structures of | ==3D structures of apoptotic protease-activating factor-1== | ||
[[Apoptotic protease-activating factor-1 3D structures]] | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:54, 9 October 2022
FunctionApoptosis protease-activating factor-1 or Apoptosis peptidase-activating factor-1 (APAF-1) binds to cytochrome c and ATP to form the apoptosome which leads to the recruitment and activation of caspase 9 by cleaving the procaspase 9. Caspase 9 is involved in executing the apoptosis of cells[1]. DiseaseInactivation of Apaf-1 is implicated in disease progression and chemoresistance of some malignancies[2]. Structural highlightsApaf-1 contains several copies of the WD-40 domain which are involved in binding to cytochrome c[3]., caspase recruitment domain (CARD) and an ATPase domain.
3D structures of apoptotic protease-activating factor-1Apoptotic protease-activating factor-1 3D structures
|
| ||||||||||
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Riedl SJ, Li W, Chao Y, Schwarzenbacher R, Shi Y. Structure of the apoptotic protease-activating factor 1 bound to ADP. Nature. 2005 Apr 14;434(7035):926-33. PMID:15829969 doi:10.1038/nature03465
- ↑ Furukawa Y, Sutheesophon K, Wada T, Nishimura M, Saito Y, Ishii H, Furukawa Y. Methylation silencing of the Apaf-1 gene in acute leukemia. Mol Cancer Res. 2005 Jun;3(6):325-34. PMID:15972851 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-04-0105
- ↑ Shalaeva DN, Dibrova DV, Galperin MY, Mulkidjanian AY. Modeling of interaction between cytochrome c and the WD domains of Apaf-1: bifurcated salt bridges underlying apoptosome assembly. Biol Direct. 2015 May 27;10:29. doi: 10.1186/s13062-015-0059-4. PMID:26014357 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13062-015-0059-4