Tripeptidyl peptidase: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
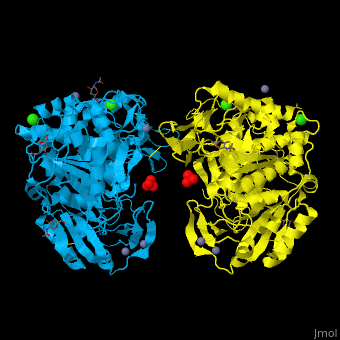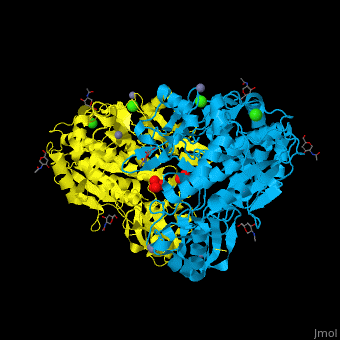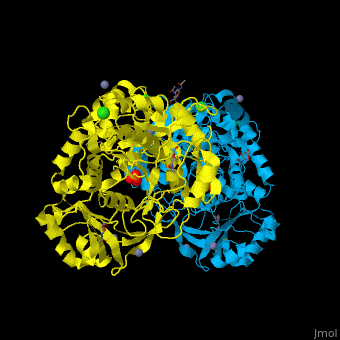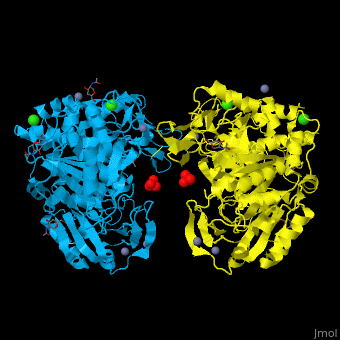
<StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Glycosylated tripeptidyl peptidase I dimer complex with sulfate, Zn+2 (grey), Ca+2 (green) and Cl- (green) ions, [[3ee6]]' scene='43/433127/Cv/5'> | |||
[[Tripeptidyl peptidase]] (TPP) is an enzyme which cleaves N-terminal tripeptides from polypeptides. TPP-I functions in lysosomes | == Function == | ||
[[Tripeptidyl peptidase]] or '''tripeptidyl aminopeptidase''' (TPP) is an enzyme which cleaves N-terminal tripeptides from polypeptides.<br /> | |||
* '''TPP-I''' functions in lysosomes<ref>PMID:29378960</ref>.<br /> | |||
* '''TPP-II''' is part of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. <br /> | |||
* '''TPP-IV''' is a serine exopeptidase which cleaves proline dipeptides from the N-terminus of polypeptides. | |||
== Didease == | |||
TPP-I participates in lysosomal turnover of proteins in pathological conditions associated with cell injury and its mutations cause the fatal neurodegenerative childhood neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis<ref>PMID:11589013</ref>. TPP-II deficiency is linked to severe autoimmunity<ref>PMID:25414442</ref>. TPP-II has central and peripheral roles in metabolism and hence in fat formation<ref>PMID:17932511</ref>. | |||
== Structural highlights == | |||
TPP-I catalytic triad is the typical <scene name='43/433127/Cv/6'>Ser-Glu-Asp</scene> and the active site contains an <scene name='43/433127/Cv/7'>octahedrally coordinated Ca+2 ion</scene><ref>PMID:19038966</ref>. | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
== 3D Structures of Tripeptidyl peptidase == | == 3D Structures of Tripeptidyl peptidase == | ||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | |||
{{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | |||
*Tripeptidyl peptidase-I | |||
**[[3ee6]] – TPP-I – human<br /> | |||
**[[3edy]] – hTPP-I precursor residues 20-563<br /> | |||
[[3ee6]] – TPP-I – human<br /> | |||
[[3edy]] – hTPP-I precursor residues 20-563 | |||
*Tripeptidyl peptidase-II | |||
[[ | **[[3lxu]] – TPP-II residues 463-770 – ''Drosophila melanogaster''<br /> | ||
*Tripeptidyl peptidase-IV | |||
**[[2eep]] – PgPro-TPP-IV+inhibitor – ''Porphyromonas gingivalis''<br /> | |||
**[[2d5l]] - PgPro-TPP-IV<br /> | |||
**[[2z3w]] - PgPro-TPP-IV (mutant)<br /> | |||
**[[2z3z]] - PgPro-TPP-IV (mutant)+inhibitor<br /> | |||
**[[2dcm]] - PgPro-TPP-IV (mutant) + substrate<br /> | |||
}} | |||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:21, 17 May 2022
FunctionTripeptidyl peptidase or tripeptidyl aminopeptidase (TPP) is an enzyme which cleaves N-terminal tripeptides from polypeptides.
DideaseTPP-I participates in lysosomal turnover of proteins in pathological conditions associated with cell injury and its mutations cause the fatal neurodegenerative childhood neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis[2]. TPP-II deficiency is linked to severe autoimmunity[3]. TPP-II has central and peripheral roles in metabolism and hence in fat formation[4]. Structural highlightsTPP-I catalytic triad is the typical and the active site contains an [5].
|
| ||||||||||
3D Structures of Tripeptidyl peptidase3D Structures of Tripeptidyl peptidase
Updated on 17-May-2022
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Sole-Domenech S, Rojas AV, Maisuradze GG, Scheraga HA, Lobel P, Maxfield FR. Lysosomal enzyme tripeptidyl peptidase 1 destabilizes fibrillar Abeta by multiple endoproteolytic cleavages within the beta-sheet domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Feb 13;115(7):1493-1498. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1719808115. Epub 2018 Jan 29. PMID:29378960 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1719808115
- ↑ Wisniewski KE, Kida E, Walus M, Wujek P, Kaczmarski W, Golabek AA. Tripeptidyl-peptidase I in neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses and other lysosomal storage disorders. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2001;5 Suppl A:73-9. PMID:11589013
- ↑ Stepensky P, Rensing-Ehl A, Gather R, Revel-Vilk S, Fischer U, Nabhani S, Beier F, Brummendorf TH, Fuchs S, Zenke S, Firat E, Pessach VM, Borkhardt A, Rakhmanov M, Keller B, Warnatz K, Eibel H, Niedermann G, Elpeleg O, Ehl S. Early-onset Evans syndrome, immunodeficiency, and premature immunosenescence associated with tripeptidyl-peptidase II deficiency. Blood. 2015 Jan 29;125(5):753-61. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-08-593202. Epub 2014, Nov 20. PMID:25414442 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-08-593202
- ↑ McKay RM, McKay JP, Suh JM, Avery L, Graff JM. Tripeptidyl peptidase II promotes fat formation in a conserved fashion. EMBO Rep. 2007 Dec;8(12):1183-9. Epub 2007 Oct 12. PMID:17932511 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.7401086
- ↑ Pal A, Kraetzner R, Gruene T, Grapp M, Schreiber K, Gronborg M, Urlaub H, Becker S, Asif AR, Gartner J, Sheldrick GM, Steinfeld R. Structure of tripeptidyl-peptidase I provides insight into the molecular basis of late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. J Biol Chem. 2009 Feb 6;284(6):3976-84. Epub 2008 Nov 26. PMID:19038966 doi:10.1074/jbc.M806947200