Pyruvate phosphate dikinase: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (156 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
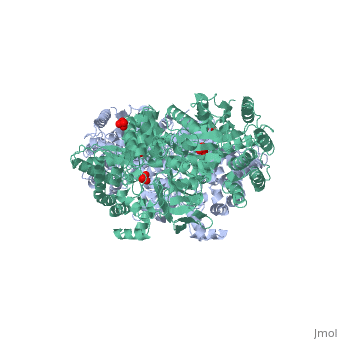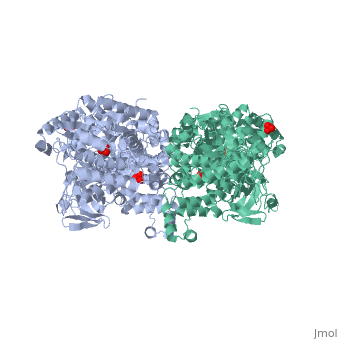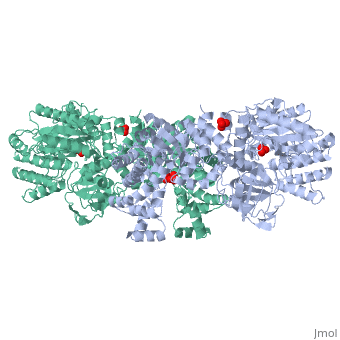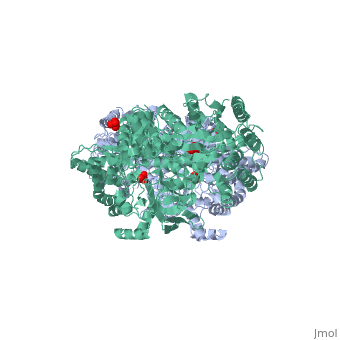
==Pyruvate phosphate dikinase | <StructureSection load='1dik' size='340' side='right' caption='Pyruvate phosphate dikinase complex with sulfate (PDB code [[1dik]])' scene=''> | ||
==Pyruvate Phosphate Dikinase - a Molecular Machine== | |||
'''Pyruvate phosphate dikinase''' (PPDK) is an enzyme that catalyzes the inter-conversion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), phosphate (P<sub>i</sub>), and pyruvate with adenine monophosphate (AMP), pyrophosphate (PP<sub>i</sub>), and phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) in the presence of magnesium and potassium/sodium ions (Mg<sup>2+</sup> and K<sup>+</sup>/Na<sup>+</sup>). The three-step reversible reaction proceeds via phosphoenzyme and pyrophosphoenzyme intermediates with a histidine residue serving as the phosphocarrier: | |||
#PPDK-His + PEP ⇄ PPDK-His~PO<sub>3</sub> + pyruvate | |||
#PPDK-His~PO<sub>3</sub> + P<sub>2</sub>O<sub>7</sub> ⇄ PPDK-His~P<sub>2</sub>O<sub>7</sub> + PO<sub>3</sub> | |||
#PPDK-His~P<sub>2</sub>O<sub>7</sub> + AMP ⇄ PPDK-His + ATP | |||
The enzyme has been found in bacteria, in C<sub>4</sub> and Crassulacean acid metabolism plants, and in parasites, but not in higher animal forms. In bacteria and parasites, PPDK functions in the direction of ATP synthesis (reminiscent of pyruvate kinase). In plants and in photosynthetic bacteria, PPDK functions in PEP formation, potentiating the rate of CO<sub>2</sub> fixation that takes place during photosynthesis. PPDK exhibits sequence homology to pyruvate phosphate synthase, and to another enzyme that utilizes phosphotransfer from PEP to a histidine residues, Enzyme I of the PEP:sugar phosphotransferase system (PTS). | |||
[[Image:1KBL dimer.png|left|150px|''PPDK dimer'']]<br />PPDK assembles into homodimers of ~95 kD subunit molecular mass. The monomer is comprised of three domains and contains two distinct reaction centers located ~45 Å apart; the PEP/pyruvate partial reaction (step 1) takes place at the C-terminal domain (adopting an α/β barrel fold) and the nucleotide and inorganic phosphate partial reactions (steps 2 and 3) take place at the N-terminal domain (adopting the ATP grasp fold with two sub domains). A central domain, tethered to the N- and C-terminal domains by two closely-associated linkers, contains a phosphorylatable histidine residue (His455). To shuttle the phosphoryl group between the two reaction centers, the His-domain undergoes domain motion of ~110° swivel around the two linkers. In addition, upon detachment from the His-domain, the two nucleotide-binding sub domains undergo a ~40° hinge motion that opens the active site cleft. | |||
|} | <br>PEP-binding domain - cyan; nucleotide binding domain - green; His-domain - yellow; domain linkers -red; phosphorylatable His455 - blue spheres|200px]] | ||
'''The His-domain in the two conformational states of PPDK. His455 is shown in blue spheres:'''[[Image:two_cond.jpg|center|500px]]<br> | |||
<p align="center"><html5media width="500" height="281" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen>https://www.youtube.com/embed/hxuBouGfs_4</html5media></p> | |||
'''''The movie''' depicts the catalytic reaction involving 3 in-line phosphotransfers & the accompanied protein conformational transitions. Model based on crystal structures of PPDK from '''Clostridium symbiosum''' in the 2 extreme conformational states shown to the left and of complexes bound to substrate analogs, phosphonopyruvate and 5'-adenylyl-β,γ-imidodiphosphate (AMPPNP). The nucleotide binding subdomains are colored green & blue, PEP binding domain colored cyan, His-domain colored yellow, and linker segments that connect the His-domain to the partner domains colored red. Ligands and the catalytic histidine are depicted in stick models with the atomic color scheme: '''''C''''' – gray, '''''N''''' – blue, '''''O''''' – red, '''''P''''' – green, '''''Mg''''' – magenta. Note that the reaction progresses in the movie in the reverse direction; steps 3 and 2 occur first followed by step 1. The movie was created by Kap Lim and Osnat Herzberg''<br> | |||
<br>You may also [http://youtu.be/hxuBouGfs_4 download] the full High Resolution video. | |||
<br> | |||
==Additional Resources== | |||
[[User:Karl_Oberholser/PPDK_large|Larger movie frame]] for classroom projection <br> | |||
For additional information, see: [[Photosynthesis]] | |||
<br /> | |||
== Key References == | |||
#Herzberg, O., Chen, C. C. H., Kapadia, G., McGuire, M., Carroll, L. J., Noh, S. J., Dunaway-Mariano, D. (1996) Swiveling-domain mechanism for enzymatic phosphotransfer between remote reaction sites, Proc Natl Acad Sci 93, 2652-2657. | |||
#Herzberg, O., Chen, C. C. H., Liu, S., Tempczyk, A., Howard, A., Wei, M., Ye, D., Dunaway-Mariano, D. (2002) Pyruvate site of pyruvate phosphate dikinase: crystal structure of the enzyme-phosphonopyruvate complex, and mutant analysis, Biochemistry 41, 780-787. | |||
#Lim, K., Read, R. J., Chen, C. C., Tempczyk, A., Wei, M., Ye, D., Wu, C., Dunaway-Mariano, D., and Herzberg, O. (2007) Swiveling domain mechanism in pyruvate phosphate dikinase, Biochemistry 46, 14845-14853. | |||
__TOC__ | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
==3D Structures of PPDK == | |||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | |||
{{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | |||
*Pyruvate phosphate dikinase | |||
**[[1vbg]] – mPPDK – maize<br /> | |||
**[[2x0s]] – PPDK – ''Trypanosoma brucei''<br /> | |||
**[[1kbl]], [[1dik]] – CsPPDK – ''Clostridium symbiosum''<br /> | |||
**[[1ggo]], [[2dik]], [[1jde]], [[2r82]] – CsPPDK (mutant)<br /> | |||
**[[2fm4]] – CsPPDK phosphoryl-carrier domain - NMR<br /> | |||
*Pyruvate phosphate dikinase complex | |||
**[[1vbh]] – mPPDK + Mg + PEP<br /> | |||
**[[5jvj]], [[5jvn]] - cyPPDK + Mg + PEP - clustered yellowtop<br /> | |||
**[[5jvl]] - cyPPDK + Mg + PEP + ATP analog<br /> | |||
**[[5lu4]] - cyPPDK + Mg + ADP + pyruvate<br /> | |||
**[[1kc7]] - CsPPDK + Mg + PEP<br /> | |||
}} | |||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:50, 9 February 2022
Pyruvate Phosphate Dikinase - a Molecular MachinePyruvate phosphate dikinase (PPDK) is an enzyme that catalyzes the inter-conversion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), phosphate (Pi), and pyruvate with adenine monophosphate (AMP), pyrophosphate (PPi), and phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) in the presence of magnesium and potassium/sodium ions (Mg2+ and K+/Na+). The three-step reversible reaction proceeds via phosphoenzyme and pyrophosphoenzyme intermediates with a histidine residue serving as the phosphocarrier:
The enzyme has been found in bacteria, in C4 and Crassulacean acid metabolism plants, and in parasites, but not in higher animal forms. In bacteria and parasites, PPDK functions in the direction of ATP synthesis (reminiscent of pyruvate kinase). In plants and in photosynthetic bacteria, PPDK functions in PEP formation, potentiating the rate of CO2 fixation that takes place during photosynthesis. PPDK exhibits sequence homology to pyruvate phosphate synthase, and to another enzyme that utilizes phosphotransfer from PEP to a histidine residues, Enzyme I of the PEP:sugar phosphotransferase system (PTS). 
The His-domain in the two conformational states of PPDK. His455 is shown in blue spheres: 
The movie depicts the catalytic reaction involving 3 in-line phosphotransfers & the accompanied protein conformational transitions. Model based on crystal structures of PPDK from Clostridium symbiosum in the 2 extreme conformational states shown to the left and of complexes bound to substrate analogs, phosphonopyruvate and 5'-adenylyl-β,γ-imidodiphosphate (AMPPNP). The nucleotide binding subdomains are colored green & blue, PEP binding domain colored cyan, His-domain colored yellow, and linker segments that connect the His-domain to the partner domains colored red. Ligands and the catalytic histidine are depicted in stick models with the atomic color scheme: C – gray, N – blue, O – red, P – green, Mg – magenta. Note that the reaction progresses in the movie in the reverse direction; steps 3 and 2 occur first followed by step 1. The movie was created by Kap Lim and Osnat Herzberg
Additional ResourcesLarger movie frame for classroom projection For additional information, see: Photosynthesis
Key References
|
| ||||||||||
3D Structures of PPDK3D Structures of PPDK
Updated on 09-February-2022