Nisin: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
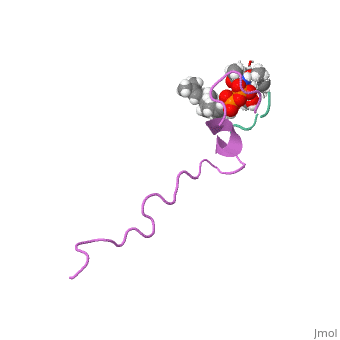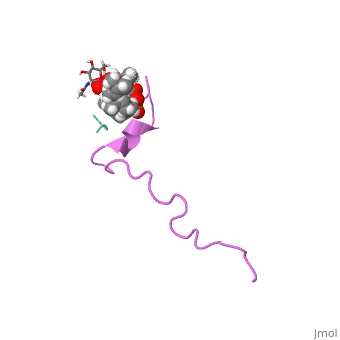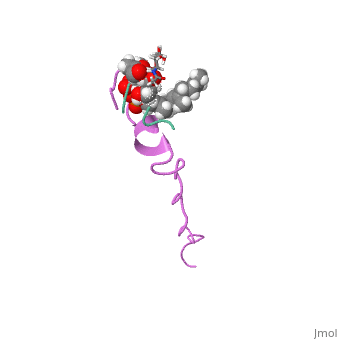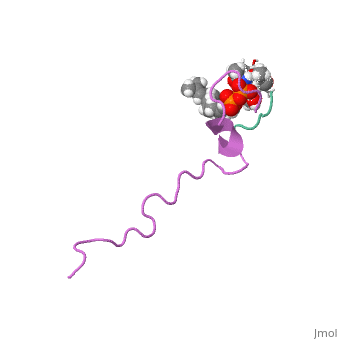
<StructureSection load=' | <StructureSection load='1wco' size='340' side='right' caption='60/607847/Nisin_structure/4 in complex with lipid (PDB code [[1wco]])' scene=''> | ||
== Function == | |||
'''Nisin''' is a polycylic antibacterial peptide, with 34 amino acid residues used as a food preservative. | |||
Nisin is produced by fermentation using the bacterium Lactococcus lactis | Nisin is produced by fermentation using the bacterium ''Lactococcus lactis''. | ||
While in general most | While in general most bacteriocins inhibit only closely related species, nisin is a rare example of a "broad-spectrum" bacteriocin effective against many Gram-positive organisms, including lactic acid bacteria (commonly associated with spoilage), ''Listeria monocytogenes'' (a known pathogen), ''Staphylococcus aureus,'' ''Bacillus cereus'', ''Clostridium botulinum'', etc. It is also particularly effective against spores. Gram-negative bacteria are protected by their outer membrane but may become susceptible to nisin action after a heat shock or when this is coupled with the chelator EDTA. Nisin is soluble in water and can be effective at levels nearing the parts-per-billion range<ref>PMID:2119570</ref>. | ||
== | == Relevance == | ||
In the food industry, it is obtained from the culturing of ''L. lactis'' on natural substrates, such as milk or dextrose, and is not chemically synthesized. Nisin is studied as a novel antibiotic due to its antimicrobial activity and as a therapeutic against neck and head squamous cell carcinoma<ref>PMID:26132406</ref>. | |||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| Line 29: | Line 27: | ||
<scene name='60/607847/Spacefill/1'>Here</scene> you can see the peptid in a spacefill presentation. | <scene name='60/607847/Spacefill/1'>Here</scene> you can see the peptid in a spacefill presentation. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== 3D structure of nisin == | |||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | |||
[[5xhb]] - LlNisin - ''Lactococcus lactis'' <br /> | |||
[[1wco]] - LlNisin + lipid - NMR<br /> | |||
[[2n32]] - LlNisin N-terminal - NMR<br /> | |||
[[2n2e]] - LlNisin C-terminal - NMR<br /> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:47, 22 November 2021
NisinNisin
FunctionNisin is a polycylic antibacterial peptide, with 34 amino acid residues used as a food preservative. Nisin is produced by fermentation using the bacterium Lactococcus lactis. While in general most bacteriocins inhibit only closely related species, nisin is a rare example of a "broad-spectrum" bacteriocin effective against many Gram-positive organisms, including lactic acid bacteria (commonly associated with spoilage), Listeria monocytogenes (a known pathogen), Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus, Clostridium botulinum, etc. It is also particularly effective against spores. Gram-negative bacteria are protected by their outer membrane but may become susceptible to nisin action after a heat shock or when this is coupled with the chelator EDTA. Nisin is soluble in water and can be effective at levels nearing the parts-per-billion range[1]. RelevanceIn the food industry, it is obtained from the culturing of L. lactis on natural substrates, such as milk or dextrose, and is not chemically synthesized. Nisin is studied as a novel antibiotic due to its antimicrobial activity and as a therapeutic against neck and head squamous cell carcinoma[2]. Structural highlightsThis is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. the structure of nisin that is available here is complex of nisin with lipid II. The origin of this structure is from lactococcus lactis.
Basic structure of nisin is presented . You can see the chain fron N (blue) to C (red). you can see the peptid in a spacefill presentation. |
| ||||||||||
3D structure of nisin3D structure of nisin
Updated on 22-November-2021
5xhb - LlNisin - Lactococcus lactis
1wco - LlNisin + lipid - NMR
2n32 - LlNisin N-terminal - NMR
2n2e - LlNisin C-terminal - NMR
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Liu W, Hansen JN. Some chemical and physical properties of nisin, a small-protein antibiotic produced by Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Aug;56(8):2551-8. PMID:2119570
- ↑ Kamarajan P, Hayami T, Matte B, Liu Y, Danciu T, Ramamoorthy A, Worden F, Kapila S, Kapila Y. Nisin ZP, a Bacteriocin and Food Preservative, Inhibits Head and Neck Cancer Tumorigenesis and Prolongs Survival. PLoS One. 2015 Jul 1;10(7):e0131008. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131008., eCollection 2015. PMID:26132406 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0131008