Muconate cycloisomerase: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
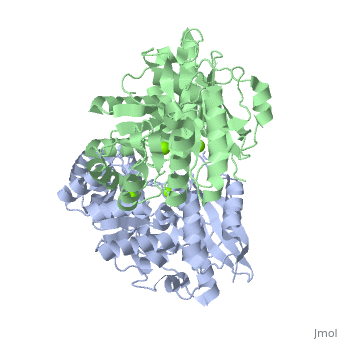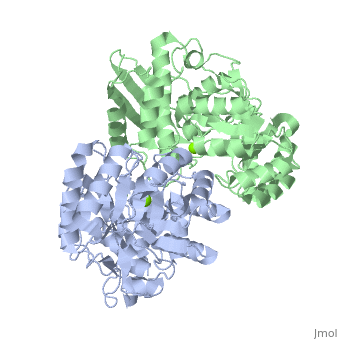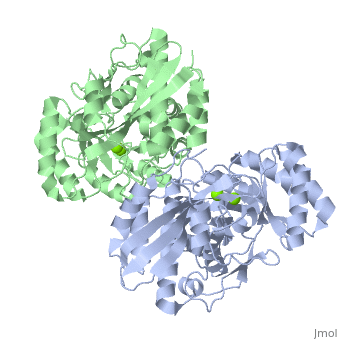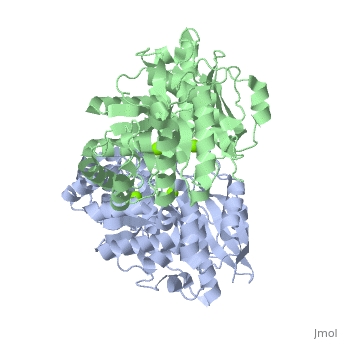
<StructureSection load='3fyy' size='350' side='right' caption='Muconate cycloisomerase dimer complex with Mg+2 ion (green) (PDB entry [[3fyy]])' scene=''> | |||
'''Muconate cycloisomerase''' (MCI) catalyzes the formation of muconolactone from ''cis,cis''-muconate. It is part of the B-ketoadipate pathway in the metabolism of aromatic compounds<ref>PMID:9726873</ref>. MCI breaks down lignin-derived catechol and protocatechuate. | '''Muconate cycloisomerase''' (MCI) catalyzes the formation of muconolactone from ''cis,cis''-muconate. It is part of the B-ketoadipate pathway in the metabolism of aromatic compounds<ref>PMID:9726873</ref>. MCI breaks down lignin-derived catechol and protocatechuate. | ||
*Chloromuconate cycloisomerase catalyzes the reversible conversion of 2-carboxy-2,5-dihydro-5-oxofuran-2-acetate to ''cis,cis''-butadiene-1,2,4-tricarboxylate <ref>PMID:7305906</ref>.<br /> | *'''Chloromuconate cycloisomerase''' catalyzes the reversible conversion of 2-carboxy-2,5-dihydro-5-oxofuran-2-acetate to ''cis,cis''-butadiene-1,2,4-tricarboxylate <ref>PMID:7305906</ref>.<br /> | ||
*3-carboxy-''cis,cis''-muconate cycloisomerase catalyzes the reversible conversion of 2-carboxy-2,5-dihydro-5-oxofuran-2-acetate to 3-chloro-''cis,cis''-muconate<ref>PMID:5916392</ref>.<br /> | *'''3-carboxy-''cis,cis''-muconate cycloisomerase''' catalyzes the reversible conversion of 2-carboxy-2,5-dihydro-5-oxofuran-2-acetate to 3-chloro-''cis,cis''-muconate<ref>PMID:5916392</ref>.<br /> | ||
</StructureSection> | |||
== 3D Structures of muconate cycloisomerase == | == 3D Structures of muconate cycloisomerase == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 16: | ||
**[[2chr]] – MCI – ''Cupriavidsua necator''<br /> | **[[2chr]] – MCI – ''Cupriavidsua necator''<br /> | ||
**[[1nu5]] - MCI – ''Pseudomonas'' | **[[1nu5]] - MCI – ''Pseudomonas''<br /> | ||
**[[4m0x]] – MCI – ''Rhodococcus opacus''<br /> | |||
*'''MCI''' | *'''MCI''' | ||
| Line 21: | Line 23: | ||
**[[1muc]], [[1bkh]] – PbMCI – ''Pseudomonas putida''<br /> | **[[1muc]], [[1bkh]] – PbMCI – ''Pseudomonas putida''<br /> | ||
**[[3muc]], [[2muc]], [[1f9c]] – PbMCI (mutant) <br /> | **[[3muc]], [[2muc]], [[1f9c]] – PbMCI (mutant) <br /> | ||
**[[3fyy]] – OiMCI – ''Oceanobacillus iheyensis''<br /> | **[[2oqy]], [[3fyy]] – OiMCI – ''Oceanobacillus iheyensis''<br /> | ||
**[[3i4k]] – MCI – ''Corynebacterium glutamicum''<br /> | **[[3i4k]] – MCI – ''Corynebacterium glutamicum''<br /> | ||
**[[3i6e]] – MCI – ''Ruegeria pomeroyi''<br /> | **[[3i6e]] – MCI – ''Ruegeria pomeroyi''<br /> | ||
| Line 28: | Line 30: | ||
**[[2zad]] – TmMCI – ''Thermotoga maritima''<br /> | **[[2zad]] – TmMCI – ''Thermotoga maritima''<br /> | ||
**[[3ct2]] - PfMCI – ''Pseudomonas fluorescens''<br /> | **[[3ct2]] - PfMCI – ''Pseudomonas fluorescens''<br /> | ||
**[[3dg3]] – MsMCI - ''Mycobacterium smegmatis'' | **[[3dg3]] – MsMCI - ''Mycobacterium smegmatis''<br /> | ||
**[[3fcp]] – MCI – ''Klebsiella pneumoniae''<br /> | |||
*MCI complexes | *MCI complexes | ||
| Line 41: | Line 44: | ||
**[[1q5n]] – MCI – ''Acinetobacter calcoaceticus''<br /> | **[[1q5n]] – MCI – ''Acinetobacter calcoaceticus''<br /> | ||
**[[1re5]] - PbMCI | **[[1re5]] - PbMCI <br /> | ||
**[[1jof]] – MCI – ''Neurospora crassa''<br /> | |||
**[[2fel]], [[2fen]] – MCI – ''Agrobacterium tumefaciens''<br /> | |||
*'''Dipeptide epimerase''' | *'''Dipeptide epimerase''' | ||
| Line 49: | Line 54: | ||
**[[3dfy]] – TmMCI<br /> | **[[3dfy]] – TmMCI<br /> | ||
**[[3q45]], [[3q4d]] – MCI + Mg + dipeptide – ''Cytophaga hutchinsonii''<br /> | **[[3q45]], [[3q4d]] – MCI + Mg + dipeptide – ''Cytophaga hutchinsonii''<br /> | ||
**[[3rit]] - MCI + Mg + dipeptide – ''Methylococcus capsulatus'' | **[[3rit]] - MCI + Mg + dipeptide – ''Methylococcus capsulatus''<br /> | ||
**[[3jva]] – EfMCI + Mg – ''Enterococcus faecalis''<br /> | |||
**[[3jw7]], [[3jzu]], [[3k1g]], [[3kum]] – EfMCI + Mg + dipeptide<br /> | |||
}} | }} | ||
== References == | |||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:31, 10 November 2021
Muconate cycloisomerase (MCI) catalyzes the formation of muconolactone from cis,cis-muconate. It is part of the B-ketoadipate pathway in the metabolism of aromatic compounds[1]. MCI breaks down lignin-derived catechol and protocatechuate.
|
| ||||||||||
3D Structures of muconate cycloisomerase3D Structures of muconate cycloisomerase
Updated on 10-November-2021
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Vollmer MD, Hoier H, Hecht HJ, Schell U, Groning J, Goldman A, Schlomann M. Substrate specificity of and product formation by muconate cycloisomerases: an analysis of wild-type enzymes and engineered variants. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1998 Sep;64(9):3290-9. PMID:9726873
- ↑ Schmidt E, Knackmuss HJ. Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenated aromatic compounds. Conversion of chlorinated muconic acids into maleoylacetic acid. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 15;192(1):339-47. PMID:7305906
- ↑ Ornston LN. The conversion of catechol and protocatechuate to beta-ketoadipate by Pseudomonas putida. II. Enzymes of the protocatechuate pathway. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3787-94. PMID:5916392