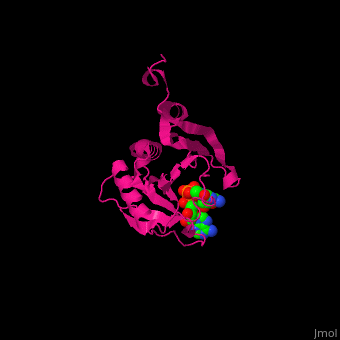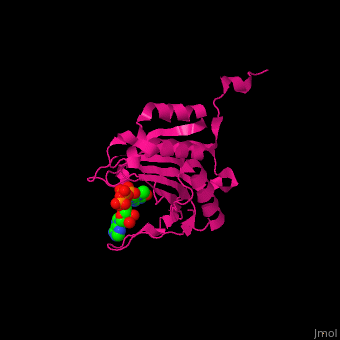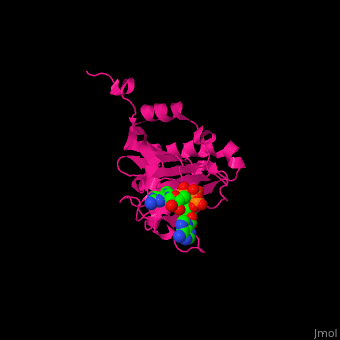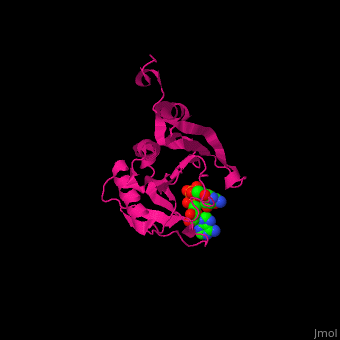Eukaryotic initiation factor: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Eukaryotic initiation factors''' (EIF) are involved in the initiation of protein translation. They form a complex with the small subunit of the ribosome and Met-tRNA which scans the mRNA and recognizes the initiation codon AUG<ref>PMID:16449648</ref>. For details | '''Eukaryotic initiation factors''' or '''Eukaryotic translation initiation factors''' (EIF) are involved in the initiation of protein translation. They form a complex with the small subunit of the ribosome and Met-tRNA which scans the mRNA and recognizes the initiation codon AUG<ref>PMID:16449648</ref>. | ||
*'''EIF1''' is implicated in the stringency of start codon selection<ref>PMID:28541577</ref>. <br /> | |||
*'''EIF2''' binds GTP and Met-tRNA and transfers Met-tRNA to the ribosomal 40S subunit<ref>PMID:10216940</ref>. <br /> | |||
*'''EIF3''' attaches to the 5'-terminal regions mRNA and scan along it to the initiation codon<ref>PMID:26344199</ref>. <br /> | |||
*'''EIF4''' recognizes the m7GpppN cap structure at the 5'-terminal of mRNA<ref>PMID:18443631</ref>. For details see [[C-terminal portion of human eIF4GI]].<br /> | |||
*'''EIF5''' is implicated in the stringency of start codon selection<ref>PMID:25114053</ref>. <br /> | |||
*'''EIF6''' is involved in maturation and/or export from the nucleus of the 60S ribosomal subunit<ref>PMID:16814427</ref>. <br /> | |||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| Line 13: | Line 20: | ||
EIF domains include the N terminal domain (NTD), C terminal domain (CTD), RNA recognition domain, middle domain, PAZ domain of EIF2C and a protein-protein interaction domain (PCI) of EIF3. | EIF domains include the N terminal domain (NTD), C terminal domain (CTD), RNA recognition domain, middle domain, PAZ domain of EIF2C and a protein-protein interaction domain (PCI) of EIF3. | ||
*<scene name='50/507723/Cv/ | *<scene name='50/507723/Cv/4'>P1-7-METHYLGUANOSINE-P3-ADENOSINE-5',5'-TRIPHOSPHATE (7-methyl GPPPA) binding site</scene>. Water molecules shown as red spheres. | ||
==3D structures of eukaryotic initiation factor== | ==3D structures of eukaryotic initiation factor== | ||
[[Eukaryotic initiation factor 3D structures]] | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:28, 20 July 2021
FunctionEukaryotic initiation factors or Eukaryotic translation initiation factors (EIF) are involved in the initiation of protein translation. They form a complex with the small subunit of the ribosome and Met-tRNA which scans the mRNA and recognizes the initiation codon AUG[1].
DiseaseOverexpression of individual subunits of eIF3 may cause malignant transformation [8]. Overexpression of eIF4g is implicated in breast cancer. Structural insightsEIF domains include the N terminal domain (NTD), C terminal domain (CTD), RNA recognition domain, middle domain, PAZ domain of EIF2C and a protein-protein interaction domain (PCI) of EIF3.
3D structures of eukaryotic initiation factorEukaryotic initiation factor 3D structures
|
| ||||||||||
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Jivotovskaya AV, Valasek L, Hinnebusch AG, Nielsen KH. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 (eIF3) and eIF2 can promote mRNA binding to 40S subunits independently of eIF4G in yeast. Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Feb;26(4):1355-72. PMID:16449648 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/MCB.26.4.1355-1372.2006
- ↑ Fijalkowska D, Verbruggen S, Ndah E, Jonckheere V, Menschaert G, Van Damme P. eIF1 modulates the recognition of suboptimal translation initiation sites and steers gene expression via uORFs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jul 27;45(13):7997-8013. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx469. PMID:28541577 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx469
- ↑ Kimball SR. Eukaryotic initiation factor eIF2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999 Jan;31(1):25-9. PMID:10216940
- ↑ des Georges A, Dhote V, Kuhn L, Hellen CU, Pestova TV, Frank J, Hashem Y. Structure of mammalian eIF3 in the context of the 43S preinitiation complex. Nature. 2015 Sep 24;525(7570):491-5. doi: 10.1038/nature14891. Epub 2015 Sep 7. PMID:26344199 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature14891
- ↑ Sonenberg N. eIF4E, the mRNA cap-binding protein: from basic discovery to translational research. Biochem Cell Biol. 2008 Apr;86(2):178-83. doi: 10.1139/O08-034. PMID:18443631 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1139/O08-034
- ↑ Saini AK, Nanda JS, Martin-Marcos P, Dong J, Zhang F, Bhardwaj M, Lorsch JR, Hinnebusch AG. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF5 promotes the accuracy of start codon recognition by regulating Pi release and conformational transitions of the preinitiation complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Sep;42(15):9623-40. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku653. Epub 2014, Aug 11. PMID:25114053 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku653
- ↑ Balbo A, Bozzaro S. Cloning of Dictyostelium eIF6 (p27BBP) and mapping its nucle(ol)ar localization subdomains. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Sep;85(9-10):1069-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.05.010. Epub, 2006 Jun 30. PMID:16814427 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.05.010
- ↑ Hershey JW. The role of eIF3 and its individual subunits in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jul;1849(7):792-800. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.10.005. Epub 2014 Nov 1. PMID:25450521 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.10.005