Complement C5: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
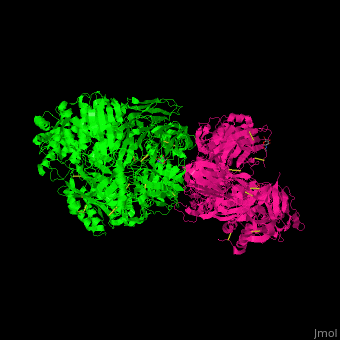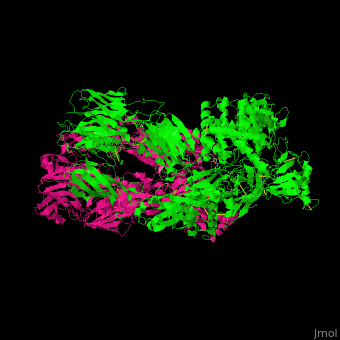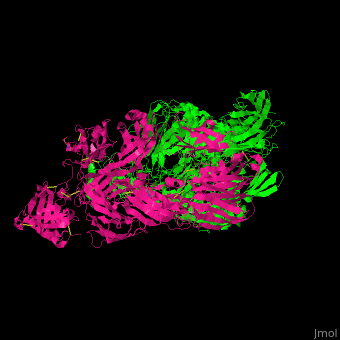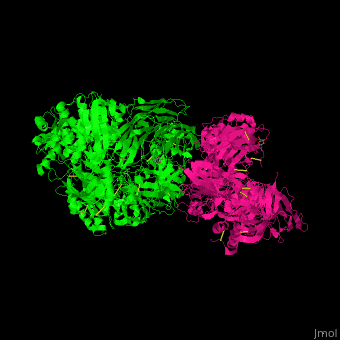
<StructureSection load=' | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Human complement C5 complex (green) with cobra venom factor (magenta) (PDB code [[3pvm]])' scene='70/705685/Cv/6'> | ||
__TOC__ | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Complement C5''' (CC5) is the fifth component of the complement system. The complement system is part of the innate immune system. CC5 is composed of α chain (C5a) and β chain (C5b). Proteoplytic degradation of CC5 produces '' | '''Complement C5''' (CC5) is the fifth component of the complement system. The complement system is part of the innate immune system. CC5 is composed of α chain (C5a) and β chain (C5b). Proteoplytic degradation of CC5 produces <scene name='70/705685/Cv/4'>anaphylatoxin</scene> which is a mediator of local inflammatory process. The C terminal domain of CC5 (residues 1530-1676) is homologous to a domain in netrins and is named <scene name='70/705685/Cv/5'>C345C</scene>. Activation of CC5 by C5 convertase initiates the assembly of the C5 to C9 components into the membrane attack complex. <ref>PMID:18536718</ref> | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Mutations in CC5 cause a deficiency leading to severe recurrent infections and are linked to liver fibrosis, Leiner's disease and rheumatoid arthritis. | Mutations in CC5 cause a deficiency leading to severe recurrent infections and are linked to liver fibrosis, Leiner's disease and rheumatoid arthritis. | ||
== 3D Structures of complement C5 == | == 3D Structures of complement C5 == | ||
[[Complement C5 3D structures]] | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | |||
Latest revision as of 09:38, 15 May 2019
FunctionComplement C5 (CC5) is the fifth component of the complement system. The complement system is part of the innate immune system. CC5 is composed of α chain (C5a) and β chain (C5b). Proteoplytic degradation of CC5 produces which is a mediator of local inflammatory process. The C terminal domain of CC5 (residues 1530-1676) is homologous to a domain in netrins and is named . Activation of CC5 by C5 convertase initiates the assembly of the C5 to C9 components into the membrane attack complex. [1] DiseaseMutations in CC5 cause a deficiency leading to severe recurrent infections and are linked to liver fibrosis, Leiner's disease and rheumatoid arthritis. 3D Structures of complement C5
|
| ||||||||||
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Fredslund F, Laursen NS, Roversi P, Jenner L, Oliveira CL, Pedersen JS, Nunn MA, Lea SM, Discipio R, Sottrup-Jensen L, Andersen GR. Structure of and influence of a tick complement inhibitor on human complement component 5. Nat Immunol. 2008 Jul;9(7):753-60. Epub 2008 Jun 8. PMID:18536718 doi:10.1038/ni.1625