Butyrylcholinesterase: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Michal Harel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (45 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
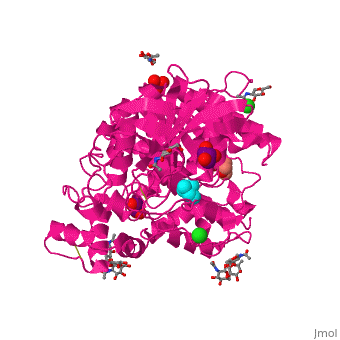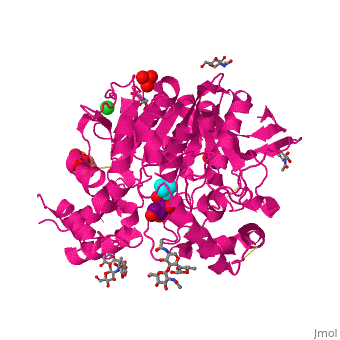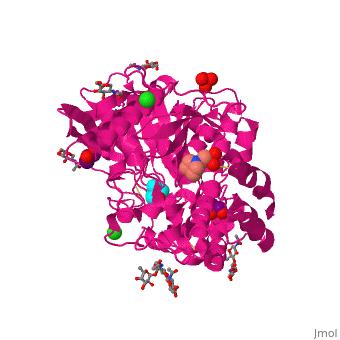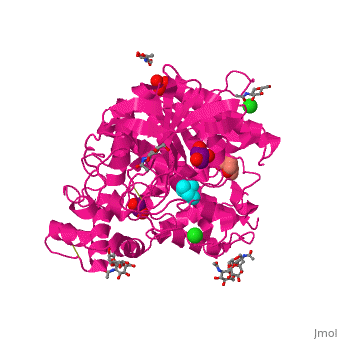
<StructureSection load='1p0m' size='350' side='right' scene='39/399020/Cv/3' caption='Glycosylated human butyrylcholinesterase complex with choline, glycerol, sulfate and Cl- ions (PDB code [[1p0m]])'> | |||
== | __TOC__ | ||
== Function == | |||
[[Butyrylcholinesterase]] (BChE) is an enzyme widely distributed throughout the body in humans, but particularly prevalent in serum, where it occurs as a tetramer of catalytic subunits. It is distinguished from the homologous enzyme, acetylcholinesterase, by its ability to hydrolyze the non-natural substrate butyrylcholine as well as the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine. <ref>PMID:12563284</ref> | |||
== | == Relevance == | ||
BChE finds medical use as a bioscavenger for overcoming organophosphate (OP) nerve agent and insecticide intoxication by interacting rapidly with the toxic agents. | |||
== | == Disease == | ||
BChE biological role remains obscure, but mutations in the human BCHE gene result in prolonged post-surgical apnea due to the inability of the mutant BChEs to hydrolyse the local anaesthetic, succinylcholine. | |||
== Structural highlights == | |||
= | Like in the AChE structure, BChE active site is located at the bottom of a ca. 20A deep gorge. The <scene name='39/399020/Cv/6'>active site of BChE</scene> is similar to that of AChE. <ref>PMID:12869558</ref> Water molecule is shown as red sphere. The differences are noticed in the lining of the gorge were some of the aromatic residues in AChE are substituted by hydrophobic ones and in the active site acyl-binding pocket where 2 Phe residues are replaced by Leu and Val in BChE. | ||
[[ | ==3D structures of BChE== | ||
[[Butyrylcholinesterase 3D structures]] | |||
</StructureSection> | |||
==Additional Resources== | ==Additional Resources== | ||
For additional information, see: [[Alzheimer's Disease]] | For additional information, see: [[Alzheimer's Disease]] | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
== References == | |||
<references/> | |||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:27, 18 April 2019
FunctionButyrylcholinesterase (BChE) is an enzyme widely distributed throughout the body in humans, but particularly prevalent in serum, where it occurs as a tetramer of catalytic subunits. It is distinguished from the homologous enzyme, acetylcholinesterase, by its ability to hydrolyze the non-natural substrate butyrylcholine as well as the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine. [1] RelevanceBChE finds medical use as a bioscavenger for overcoming organophosphate (OP) nerve agent and insecticide intoxication by interacting rapidly with the toxic agents. DiseaseBChE biological role remains obscure, but mutations in the human BCHE gene result in prolonged post-surgical apnea due to the inability of the mutant BChEs to hydrolyse the local anaesthetic, succinylcholine. Structural highlightsLike in the AChE structure, BChE active site is located at the bottom of a ca. 20A deep gorge. The is similar to that of AChE. [2] Water molecule is shown as red sphere. The differences are noticed in the lining of the gorge were some of the aromatic residues in AChE are substituted by hydrophobic ones and in the active site acyl-binding pocket where 2 Phe residues are replaced by Leu and Val in BChE. 3D structures of BChEButyrylcholinesterase 3D structures
|
| ||||||||||
Additional ResourcesAdditional Resources
For additional information, see: Alzheimer's Disease
ReferencesReferences
- ↑ Darvesh S, Hopkins DA, Geula C. Neurobiology of butyrylcholinesterase. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003 Feb;4(2):131-8. PMID:12563284 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrn1035
- ↑ Nicolet Y, Lockridge O, Masson P, Fontecilla-Camps JC, Nachon F. Crystal structure of human butyrylcholinesterase and of its complexes with substrate and products. J Biol Chem. 2003 Oct 17;278(42):41141-7. Epub 2003 Jul 17. PMID:12869558 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M210241200