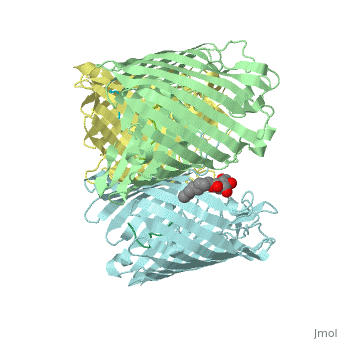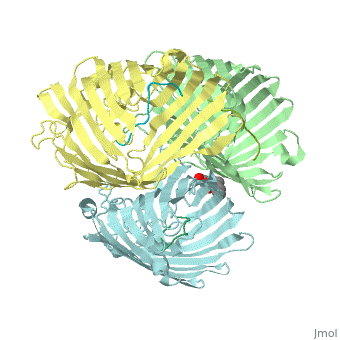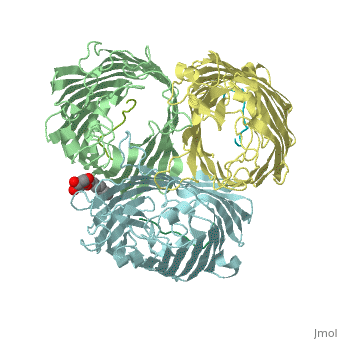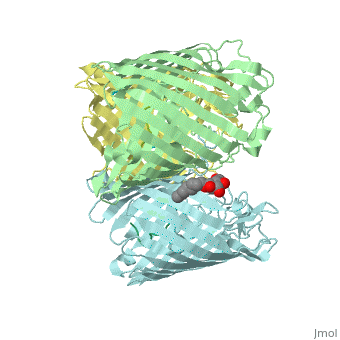3o0e
Crystal structure of OmpF in complex with colicin peptide OBS1Crystal structure of OmpF in complex with colicin peptide OBS1
Structural highlights
FunctionOMPF_ECOLI Forms pores that allow passive diffusion of small molecules across the outer membrane. It is also a receptor for the bacteriophage T2.[1] Publication Abstract from PubMedThe porins OmpF and OmpC are trimeric beta-barrel proteins with narrow channels running through each monomer that exclude molecules > 600 Da while mediating the passive diffusion of small nutrients and metabolites across the Gram-negative outer membrane (OM). Here, we elucidate the mechanism by which an entire soluble protein domain (> 6 kDa) is delivered through the lumen of such porins. Following high-affinity binding to the vitamin B(12) receptor in Escherichia coli, the bacteriocin ColE9 recruits OmpF or OmpC using an 83-residue intrinsically unstructured translocation domain (IUTD) to deliver a 16-residue TolB-binding epitope (TBE) in the center of the IUTD to the periplasm where it triggers toxin entry. We demonstrate that the IUTD houses two OmpF-binding sites, OBS1 (residues 2-18) and OBS2 (residues 54-63), which flank the TBE and bind with K(d)s of 2 and 24 muM, respectively, at pH 6.5 and 25 masculineC. We show the two OBSs share the same binding site on OmpF and that the colicin must house at least one of them for antibiotic activity. Finally, we report the structure of the OmpF-OBS1 complex that shows the colicin bound within the porin lumen spanning the membrane bilayer. Our study explains how colicins exploit porins to deliver epitope signals to the bacterial periplasm and, more broadly, how the inherent flexibility and narrow cross-sectional area of an IUP domain can endow it with the ability to traverse a biological membrane via the constricted lumen of a beta-barrel membrane protein. Directed epitope delivery across the Escherichia coli outer membrane through the porin OmpF.,Housden NG, Wojdyla JA, Korczynska J, Grishkovskaya I, Kirkpatrick N, Brzozowski AM, Kleanthous C Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Nov 22. PMID:21098297[2] From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. See AlsoReferences
|
| ||||||||||||||||||